Betulinic acid suppresses constitutive and TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and induces apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells
- PMID: 18444250
- PMCID: PMC2864721
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20447
Betulinic acid suppresses constitutive and TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and induces apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells
Abstract
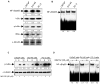
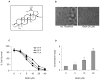
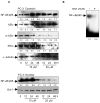
Development of chemoresistance in androgen-refractory prostate cancer cells is partly due to constitutive activation of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors that regulate several cell survival and anti-apoptotic genes. In this study we examined whether betulinic acid (BetA), a pentacyclic triterpene from the bark of white birch, is effective in inhibiting NF-kappaB expression in androgen-refractory human prostate cancer cells exhibiting high constitutive NF-kappaB expression. Treatment of PC-3 cells with BetA inhibited DNA binding and reduced nuclear levels of the NF-kappaB/p65. BetA-mediated NF-kappaB inhibition involved decreased IKK activity and phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha at serine 32/36 followed by its degradation. Reporter assays revealed that NF-kappaB inhibition by BetA is transcriptionally active. These effects were found to correlate with a shift in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and cleavage of poly(ADP)ribose polymerase more towards apoptosis. BetA also inhibited TNFalpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB via the IkappaBalpha pathway, thereby sensitizing the cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Our studies demonstrate that BetA effectively inhibits constitutive NF-kappaB activation and supports the rationale for targeting NF-kappaB through combination protocols with BetA in androgen-refractory prostate cancer.
Figures
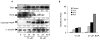
Similar articles
-
Suppression of constitutive and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation and induction of apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells: correlation with down-regulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 May 1;10(9):3169-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0586. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15131058
-
Betulinic Acid-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells Involves p53 and Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathways.Molecules. 2017 Feb 10;22(2):264. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020264. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28208611 Free PMC article.
-
Betulinic acid suppresses carcinogen-induced NF-kappa B activation through inhibition of I kappa B alpha kinase and p65 phosphorylation: abrogation of cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloprotease-9.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 15;171(6):3278-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3278. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12960358
-
Betulinic acid, a natural compound with potent anticancer effects.Anticancer Drugs. 2010 Mar;21(3):215-27. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283357c62. Anticancer Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20075711 Review.
-
Betulinic acid: a natural product with anticancer activity.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009 Jan;53(1):140-6. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700491. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009. PMID: 19065582 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Stem Bark of Alstonia boonei De Wild. (Apocynaceae) on Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Wistar Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 30;2020:4918453. doi: 10.1155/2020/4918453. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32565862 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic combination of gemcitabine and dietary molecule induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells and down regulates PKM2 expression.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 8;9(9):e107154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107154. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25197966 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and In Vivo Antiarthritic Activities of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Dissotis thollonii Cogn. (Melastomataceae) in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 15;2019:3612481. doi: 10.1155/2019/3612481. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31827550 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic investigation into betulinic acid-induced apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cells.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 22;9(8):e105768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105768. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25148076 Free PMC article.
-
Selected Extracts of Chinese Herbal Medicines: Their Effect on NF-κB, PPARα and PPARγ and the Respective Bioactive Compounds.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:983023. doi: 10.1155/2012/983023. Epub 2012 May 23. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22675394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:725–734. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441:431–436. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 2006;2:6680–6684. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Stark GR. NFkappaB-dependent signaling pathways. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:285–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

