siRNA-mediated reduction of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB kinase prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle
- PMID: 18443205
- PMCID: PMC2494681
- DOI: 10.2337/db07-0763
siRNA-mediated reduction of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB kinase prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle
Abstract
Objective: Proinflammatory cytokines contribute to systemic low-grade inflammation and insulin resistance. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha impedes insulin signaling in insulin target tissues. We determined the role of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB kinase (IKK)beta in TNF-alpha-induced impairments in insulin signaling and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle.
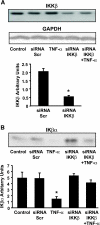
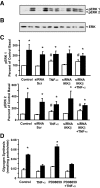
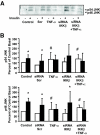
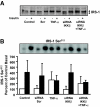
Research design and methods: Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to silence IKKbeta gene expression in primary human skeletal muscle myotubes from nondiabetic subjects. siRNA gene silencing reduced IKKbeta protein expression 73% (P < 0.05). Myotubes were incubated in the absence or presence of insulin and/or TNF-alpha, and effects of IKKbeta silencing on insulin signaling and glucose metabolism were determined.
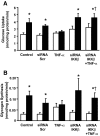
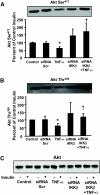
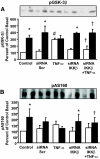
Results: Insulin increased glucose uptake 1.7-fold (P < 0.05) and glucose incorporation into glycogen 3.8-fold (P < 0.05) in myotubes from nondiabetic subjects. TNF-alpha exposure fully impaired insulin-mediated glucose uptake and metabolism. IKKbeta siRNA protected against TNF-alpha-induced impairments in glucose metabolism, since insulin-induced increases in glucose uptake (1.5-fold; P < 0.05) and glycogen synthesis (3.5-fold; P < 0.05) were restored. Conversely, TNF-alpha-induced increases in insulin receptor substrate-1 serine phosphorylation (Ser(312)), Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase phosphorylation, and extracellular signal-related kinase-1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation were unaltered by siRNA-mediated IKKbeta reduction. siRNA-mediated IKKbeta reduction prevented TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance on Akt Ser(473) and Thr(308) phosphorylation and phosphorylation of the 160-kDa Akt substrate AS160. IKKbeta silencing had no effect on cell differentiation. Finally, mRNA expression of GLUT1 or GLUT4 and protein expression of MAPK kinase kinase kinase isoform 4 (MAP4K4) was unaltered by IKKbeta siRNA.
Conclusions: IKKbeta silencing prevents TNF-alpha-induced impairments in insulin action on Akt phosphorylation and glucose uptake and metabolism in human skeletal muscle.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MAP4K4 gene silencing in human skeletal muscle prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 16;282(11):7783-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608602200. Epub 2007 Jan 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17227768
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha produces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by activation of inhibitor kappaB kinase in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17070-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312021200. Epub 2004 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14764603
-
Classical NF-κB activation impairs skeletal muscle oxidative phenotype by reducing IKK-α expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1842(2):175-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24215713
-
Insulin resistance induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in myocytes and brown adipocytes.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E94-104. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0462. Epub 2007 Oct 16. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 17940160 Review.
-
Androgens and skeletal muscle: cellular and molecular action mechanisms underlying the anabolic actions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 May;69(10):1651-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0883-3. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22101547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implication of inflammatory signaling pathways in obesity-induced insulin resistance.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Jan 8;3:181. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00181. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 23316186 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hepatic fat accumulation in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Apr 28;9:42. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-42. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20426802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary exercise as a novel strategy for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome: effects on skeletal muscle function.J Nutr Metab. 2011;2011:676208. doi: 10.1155/2011/676208. Epub 2011 Jun 6. J Nutr Metab. 2011. PMID: 21773023 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated View of Immunometabolism.Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):22-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.025. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29328913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 intensive-care patients: Mechanism and treatment strategy.Prim Care Diabetes. 2021 Jun;15(3):409-416. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33436320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Plomgaard P, Bouzakri K, Krogh-Madsen R, Mittendorfer B, Zierath JR, Pedersen BK: Tumor necrosis factor-α induces skeletal muscle insulin resistance in healthy human subjects via inhibition of Akt substrate 160 phosphorylation. Diabetes 54: 2939–2945, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Yin MJ, Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB: The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature 396: 77–80, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen L, Li ZW, Karin M, Shoelson SE: Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkbeta. Science 293: 1673–1677, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Ruotsalainen E, Salmenniemi U, Vauhkonen I, Pihlajamaki J, Punnonen K, Kainulainen S, Laakso M: Changes in inflammatory cytokines are related to impaired glucose tolerance in offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 29: 2714–2720, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

