Aurora B kinase and protein phosphatase 1 have opposing roles in modulating kinetochore assembly
- PMID: 18426974
- PMCID: PMC2315672
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200710019
Aurora B kinase and protein phosphatase 1 have opposing roles in modulating kinetochore assembly
Abstract
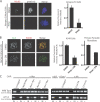
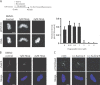
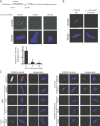
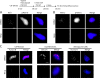
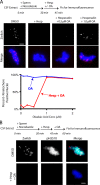
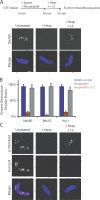
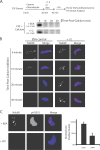
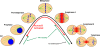
The outer kinetochore binds microtubules to control chromosome movement. Outer kinetochore assembly is restricted to mitosis, whereas the inner kinetochore remains tethered to centromeres throughout the cell cycle. The cues that regulate this transient assembly are unknown. We find that inhibition of Aurora B kinase significantly reduces outer kinetochore assembly in Xenopus laevis and human tissue culture cells, frog egg extracts, and budding yeast. In X. leavis M phase extracts, preassembled kinetochores disassemble after inhibiting Aurora B activity with either drugs or antibodies. Kinetochore disassembly, induced by Aurora B inhibition, is rescued by restraining protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) activity. PP1 is necessary for kinetochores to disassemble at the exit from M phase, and purified enzyme is sufficient to cause disassembly on isolated mitotic nuclei. These data demonstrate that Aurora B activity is required for kinetochore maintenance and that PP1 is necessary and sufficient to disassemble kinetochores. We suggest that Aurora B and PP1 coordinate cell cycle-dependent changes in kinetochore assembly though phosphorylation of kinetochore substrates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enrichment of Aurora B kinase at the inner kinetochore controls outer kinetochore assembly.J Cell Biol. 2019 Oct 7;218(10):3237-3257. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201901004. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31527147 Free PMC article.
-
Sds22 regulates aurora B activity and microtubule-kinetochore interactions at mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Oct 4;191(1):61-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912046. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20921135 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated targeting of protein phosphatase 1 to the outer kinetochore by KNL1 opposes Aurora B kinase.J Cell Biol. 2010 Mar 22;188(6):809-20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001006. Epub 2010 Mar 15. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20231380 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between mitotic kinesins and the Aurora kinase-PP1 (protein phosphatase 1) axis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Dec;41(6):1761-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20130191. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 24256288 Review.
-
The right place at the right time: Aurora B kinase localization to centromeres and kinetochores.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 4;64(2):299-311. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190081. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32406506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Borealin directs recruitment of the CPC to oocyte chromosomes and movement to the microtubules.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e202006018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202006018. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33836043 Free PMC article.
-
The aurora B kinase promotes inner and outer kinetochore interactions in budding yeast.Genetics. 2013 Jul;194(3):785-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.150839. Epub 2013 May 1. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23636741 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of Aurora B kinase at the inner kinetochore controls outer kinetochore assembly.J Cell Biol. 2019 Oct 7;218(10):3237-3257. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201901004. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31527147 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatases: providing safe passage through mitotic exit.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul 13;12(8):469-82. doi: 10.1038/nrm3149. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21750572 Review.
-
RanBP2 and SENP3 function in a mitotic SUMO2/3 conjugation-deconjugation cycle on Borealin.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):410-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-05-0511. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 18946085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brautigan, D.L., C.L. Shriner, and P.A. Gruppuso. 1985. Phosphorylase phosphatase catalytic subunit. Evidence that the Mr = 33,000 enzyme fragment is derived from a native protein of Mr = 70,000. J. Biol. Chem. 260:4295–4302. - PubMed
-
- Brautigan, D.L., J. Sunwoo, J.C. Labbe, A. Fernandez, and N.J. Lamb. 1990. Cell cycle oscillation of phosphatase inhibitor-2 in rat fibroblasts coincident with p34cdc2 restriction. Nature. 344:74–78. - PubMed
-
- Cheeseman, I.M., S. Anderson, M. Jwa, E.M. Green, J. Kang, J.R. Yates III, C.S. Chan, D.G. Drubin, and G. Barnes. 2002. Phospho-regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments by the Aurora kinase Ipl1p. Cell. 111:163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

