TNF-alpha stimulation inhibits siRNA-mediated RNA interference through a mechanism involving poly-(A) tail stabilization
- PMID: 18423387
- PMCID: PMC2646504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.03.007
TNF-alpha stimulation inhibits siRNA-mediated RNA interference through a mechanism involving poly-(A) tail stabilization
Abstract
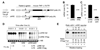
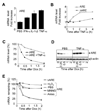
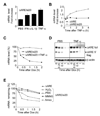
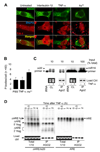
The control of mRNA stability is a complex biological process that involves numerous factors, including microRNA (miRNA) and short interfering RNA (siRNA). Here, we show that short interfering RNA (siRNA) and microRNA share some similarities in their response to cellular stress. miR16 expedites the degradation of mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (ARE) in their 3' untranslated region (UTR). si20 is an siRNA designed to target a non-ARE sequence in the TNF 3'UTR. We found that both si20 and miR16/ARE-mediated degradation of mRNAs can be inhibited by stimulating cells with different stresses. By analyzing TNF-alpha stimulation-mediated stabilization of si20- and miR16-targeted mRNA, we show that this stabilization is not caused by modifying si20 and miR16 loading into Ago2 complexes, or mRNA targeting to Ago2, but by inhibiting mRNA deadenylation. This is the first report showing that a specific siRNA-mediated mRNA degradation can be regulated by inflammatory stimuli, and that deadenylation is involved in this siRNA-mediated mRNA decay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Translation repression in human cells by microRNA-induced gene silencing requires RCK/p54.PLoS Biol. 2006 Jul;4(7):e210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040210. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 16756390 Free PMC article.
-
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase stabilizes mRNAs that contain cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor AU-rich elements by inhibiting deadenylation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 10;278(41):39470-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306345200. Epub 2003 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12882963
-
Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA instability.Cell. 2005 Mar 11;120(5):623-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.038. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15766526
-
Mechanisms of deadenylation-dependent decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):167-83. doi: 10.1002/wrna.40. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Messenger RNA turnover in eukaryotes: pathways and enzymes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Jul-Aug;39(4):197-216. doi: 10.1080/10409230490513991. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15596551 Review.
Cited by
-
Tristetraprolin (TTP): interactions with mRNA and proteins, and current thoughts on mechanisms of action.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):666-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23428348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROCK inhibition enhances microRNA function by promoting deadenylation of targeted mRNAs via increasing PAIP2 expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):7577-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv728. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26187994 Free PMC article.
-
A daphnane diterpenoid isolated from Wikstroemia polyantha induces an inflammatory response and modulates miRNA activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039621. Epub 2012 Jun 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761847 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

