Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response are linked to synergistic IFN-beta induction via X-box binding protein 1
- PMID: 18412159
- PMCID: PMC2838478
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200737882
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response are linked to synergistic IFN-beta induction via X-box binding protein 1
Abstract
Type I IFN are strongly induced upon engagement of certain pattern recognition receptors by microbial products, and play key roles in regulating innate and adaptive immunity. It has become apparent that the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced unfolded protein response (UPR), in addition to restoring ER homeostasis, also influences the expression of certain inflammatory cytokines. However, the extent to which UPR signaling regulates type I IFN remains unclear. Here we show that cells undergoing a UPR respond to TLR4 and TLR3 ligands, and intracellular dsRNA, with log-fold greater IFN-beta induction. This synergy is not dependent on autocrine type I IFN signaling, but unexpectedly requires the UPR transcription factor X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1). Synergistic IFN-beta induction also occurs in HLA-B27/human beta(2)m-transgenic rat macrophages exhibiting a UPR as a consequence of HLA-B27 up-regulation, where it correlates with activation of XBP-1 splicing. Together these findings indicate that the cellular response to endogenous 'danger' that disrupts ER homeostasis is coupled to IFN-beta induction by XBP-1, which has implications for the immune response and the pathogenesis of diseases involving the UPR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
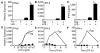
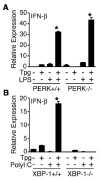
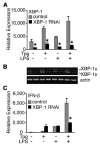
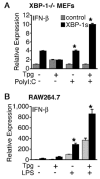
 indicates Tpg plus LPS. IFN transcript levels were measured with qPCR and are shown normalized to GAPDH. Results shown are means ±SD (A–C) and are representative of 4 (Tm) or 5 (Tpg) experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate p<0.05 for average fold induction for LPS plus Tpg (or Tm) vs. LPS alone, from combined experiments. Concentration curve and time course (D–F) are representative of two experiments.
indicates Tpg plus LPS. IFN transcript levels were measured with qPCR and are shown normalized to GAPDH. Results shown are means ±SD (A–C) and are representative of 4 (Tm) or 5 (Tpg) experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate p<0.05 for average fold induction for LPS plus Tpg (or Tm) vs. LPS alone, from combined experiments. Concentration curve and time course (D–F) are representative of two experiments.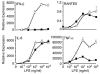
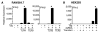
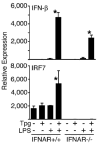
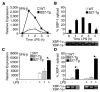
 ) were activated with IFN-γ for 20 h, then stimulated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 1–4 h. (A) Relative IFN-β transcripts were measured by qPCR. In (B), XBP-1 splicing in WT (
) were activated with IFN-γ for 20 h, then stimulated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 1–4 h. (A) Relative IFN-β transcripts were measured by qPCR. In (B), XBP-1 splicing in WT ( ) and B27-Tg (ν) macrophages was determined as described in the legend to Figure 6. IFN-γ activated macrophages from Lewis WT (
) and B27-Tg (ν) macrophages was determined as described in the legend to Figure 6. IFN-γ activated macrophages from Lewis WT ( ), B7-Tg(■), or B27-Tg (ν) rats, were stimulated with LPS for 2 h. IFN-β message levels were determined by qPCR (C) and XBP-1 splicing by PCR (D) as in (B). Results in A are the average of duplicates and are representative of 3 experiments. Results shown in B-D are mean ±SD and are representative of at least 2 experiments. In (B) p<0.05 for B27-Tg vs. WT, where it is barely detected. In (C and D) asterisks (*) indicate p<0.05 for B27-Tg vs. B7-Tg and WT. Representative XBP-1 splicing gel lanes in B and D are in the same sequence as the quantitative data.
), B7-Tg(■), or B27-Tg (ν) rats, were stimulated with LPS for 2 h. IFN-β message levels were determined by qPCR (C) and XBP-1 splicing by PCR (D) as in (B). Results in A are the average of duplicates and are representative of 3 experiments. Results shown in B-D are mean ±SD and are representative of at least 2 experiments. In (B) p<0.05 for B27-Tg vs. WT, where it is barely detected. In (C and D) asterisks (*) indicate p<0.05 for B27-Tg vs. B7-Tg and WT. Representative XBP-1 splicing gel lanes in B and D are in the same sequence as the quantitative data.Similar articles
-
XBP-1 couples endoplasmic reticulum stress to augmented IFN-beta induction via a cis-acting enhancer in macrophages.J Immunol. 2010 Aug 15;185(4):2324-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903052. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20660350 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum degradation-enhancing α-mannosidase-like protein 1 targets misfolded HLA-B27 dimers for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Nov;66(11):2976-88. doi: 10.1002/art.38809. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25132672 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-B27 up-regulation causes accumulation of misfolded heavy chains and correlates with the magnitude of the unfolded protein response in transgenic rats: Implications for the pathogenesis of spondylarthritis-like disease.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Jan;56(1):215-23. doi: 10.1002/art.22295. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17195225
-
HLA-B27 misfolding and ankylosing spondylitis.Mol Immunol. 2014 Jan;57(1):44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23993278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Cytokine Production by the Unfolded Protein Response; Implications for Infection and Autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 5;9:422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00422. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29556237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Autophagy-Related Proteins in Candida albicans Infections.Pathogens. 2016 Mar 29;5(2):34. doi: 10.3390/pathogens5020034. Pathogens. 2016. PMID: 27043636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying novel spatiotemporal regulators of innate immunity.Immunol Res. 2013 Mar;55(1-3):3-9. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8344-0. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 22926826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthmatic lung fibroblasts promote type 2 immune responses via endoplasmic reticulum stress response dependent thymic stromal lymphopoietin secretion.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 25;14:1064822. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1064822. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36760534 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Maternal Air Pollution Exposure on Children's Lung Health: An Indian Perspective.Toxics. 2018 Nov 16;6(4):68. doi: 10.3390/toxics6040068. Toxics. 2018. PMID: 30453488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum calcium depletion impacts chaperone secretion, innate immunity, and phagocytic uptake of cells.J Immunol. 2011 Jul 15;187(2):919-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100690. Epub 2011 Jun 13. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21670312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–336. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi T, Takaoka A. A weak signal for strong responses: interferon-alpha/beta revisited. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:378–386. - PubMed
-
- Mitani Y, Takaoka A, Kim SH, Kato Y, Yokochi T, Tanaka N, Taniguchi T. Cross talk of the interferon-alpha/beta signalling complex with gp130 for effective interleukin-6 signalling. Genes Cells. 2001;6:631–640. - PubMed
-
- Takaoka A, Mitani Y, Suemori H, Sato M, Yokochi T, Noguchi S, Tanaka N, Taniguchi T. Cross talk between interferon-gamma and -alpha/beta signaling components in caveolar membrane domains. Science. 2000;288:2357–2360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

