Phosphorylation of SDT repeats in the MDC1 N terminus triggers retention of NBS1 at the DNA damage-modified chromatin
- PMID: 18411307
- PMCID: PMC2315670
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200708210
Phosphorylation of SDT repeats in the MDC1 N terminus triggers retention of NBS1 at the DNA damage-modified chromatin
Abstract
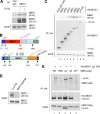
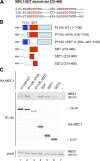
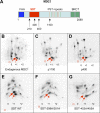
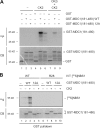
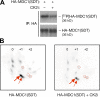
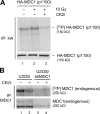
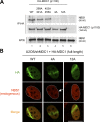
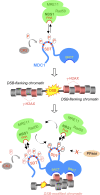
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) trigger accumulation of the MRE11-RAD50-Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (NBS1 [MRN]) complex, whose retention on the DSB-flanking chromatin facilitates survival. Chromatin retention of MRN requires the MDC1 adaptor protein, but the mechanism behind the MRN-MDC1 interaction is unknown. We show that the NBS1 subunit of MRN interacts with the MDC1 N terminus enriched in Ser-Asp-Thr (SDT) repeats. This interaction was constitutive and mediated by binding between the phosphorylated SDT repeats of MDC1 and the phosphate-binding forkhead-associated domain of NBS1. Phosphorylation of the SDT repeats by casein kinase 2 (CK2) was sufficient to trigger MDC1-NBS1 interaction in vitro, and MDC1 associated with CK2 activity in cells. Inhibition of CK2 reduced SDT phosphorylation in vivo, and disruption of the SDT-associated phosphoacceptor sites prevented the retention of NBS1 at DSBs. Together, these data suggest that phosphorylation of the SDT repeats in the MDC1 N terminus functions to recruit NBS1 and, thereby, increases the local concentration of MRN at the sites of chromosomal breakage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phospho-dependent interactions between NBS1 and MDC1 mediate chromatin retention of the MRN complex at sites of DNA damage.EMBO Rep. 2008 Aug;9(8):795-801. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.103. Epub 2008 Jun 27. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18583988 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive phosphorylation of MDC1 physically links the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex to damaged chromatin.J Cell Biol. 2008 Apr 21;181(2):227-40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709008. Epub 2008 Apr 14. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18411308 Free PMC article.
-
MDC1 regulates intra-S-phase checkpoint by targeting NBS1 to DNA double-strand breaks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 12;105(32):11200-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802885105. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18678890 Free PMC article.
-
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 is a keystone complex connecting DNA repair machinery, double-strand break signaling, and the chromatin template.Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;85(4):509-20. doi: 10.1139/O07-069. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713585 Review.
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder (ATLD)-its clinical presentation and molecular basis.DNA Repair (Amst). 2004 Aug-Sep;3(8-9):1219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.04.009. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004. PMID: 15279810 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of H2AX on lysine 36 plays a key role in the DNA double-strand break repair pathway.FEBS Lett. 2010 Jul 2;584(13):2926-30. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.05.017. Epub 2010 May 17. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20488183 Free PMC article.
-
ATM protein-dependent phosphorylation of Rad50 protein regulates DNA repair and cell cycle control.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 9;286(36):31542-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.258152. Epub 2011 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757780 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-Ser/Thr-binding domains: navigating the cell cycle and DNA damage response.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;14(9):563-80. doi: 10.1038/nrm3640. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23969844 Review.
-
Immediate-Early, Early, and Late Responses to DNA Double Stranded Breaks.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 31;13:793884. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.793884. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35173769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-regulated binding of Ctp1 to Nbs1 is critical for repair of DNA double-strand breaks.Cell Cycle. 2010 Apr 15;9(8):1516-22. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.8.11260. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20421724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartek, J., and J. Lukas. 2007. DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19:238–245. - PubMed
-
- Bekker-Jensen, S., K. Fugger, J.R. Danielsen, I. Gromova, M. Sehested, J. Celis, J. Bartek, J. Lukas, and N. Mailand. 2007. Human Xip1 (C2orf13) is a novel regulator of cellular responses to DNA strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 282:19638–19643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

