Human cytomegalovirus protein UL38 inhibits host cell stress responses by antagonizing the tuberous sclerosis protein complex
- PMID: 18407068
- PMCID: PMC2759192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.03.002
Human cytomegalovirus protein UL38 inhibits host cell stress responses by antagonizing the tuberous sclerosis protein complex
Abstract
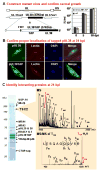
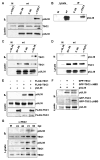
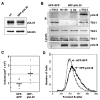
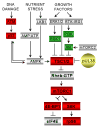
Human cytomegalovirus proteins alter host cells to favor virus replication. These viral proteins include pUL38, which prevents apoptosis. To characterize the mode of action of pUL38, we modified the viral genome to encode an epitope-tagged pUL38 and used rapid immunoaffinity purification to isolate pUL38-interacting host proteins, which were then identified by mass spectrometry. One of the cellular proteins identified was TSC2, a constituent of the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressor protein complex (TSC1/2). TSC1/2 integrates stress signals and regulates the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein complex that responds to stress by limiting protein synthesis and cell growth. We showed that pUL38 interacts with TSC1 and TSC2 in cells infected with wild-type cytomegalovirus. Furthermore, TSC1/2 failed to regulate mTORC1 in cells expressing pUL38, and these cells exhibited the enlarged size characteristic of cytomegalovirus infection. Thus, pUL38 supports virus replication at least in part by blocking cellular responses to stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Protein 2-Independent Activation of mTORC1 by Human Cytomegalovirus pUL38.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7625-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01027-15. Epub 2015 May 13. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25972538 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus protein pUL38 suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death independently of its ability to induce mTORC1 activation.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):9103-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00572-11. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21715486 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type-dependent regulation of mTORC1 by REDD1 and the tumor suppressors TSC1/TSC2 and LKB1 in response to hypoxia.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 May;31(9):1870-84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01393-10. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21383064 Free PMC article.
-
Mourning Dr. Alfred G. Knudson: the two-hit hypothesis, tumor suppressor genes, and the tuberous sclerosis complex.Cancer Sci. 2017 Jan;108(1):5-11. doi: 10.1111/cas.13116. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 27862655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tsc1-Tsc2 complex influences neuronal polarity by modulating TORC1 activity and SAD levels.Genes Dev. 2008 Sep 15;22(18):2447-53. doi: 10.1101/gad.1724108. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18794342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics in drug target discovery.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011;76:235-46. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010694. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011. PMID: 22114327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is human cytomegalovirus a target in cancer therapy?Oncotarget. 2011 Dec;2(12):1329-38. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.383. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 22246171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minding the message: tactics controlling RNA decay, modification, and translation in virus-infected cells.Genes Dev. 2022 Feb 1;36(3-4):108-132. doi: 10.1101/gad.349276.121. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 35193946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meal for Two: Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Activation of Cellular Metabolism.Viruses. 2019 Mar 19;11(3):273. doi: 10.3390/v11030273. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30893762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The changing role of mTOR kinase in the maintenance of protein synthesis during human cytomegalovirus infection.J Virol. 2011 Apr;85(8):3930-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01913-10. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21307192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowen NJ, Fujita N, Kajita M, Wade PA. Mi-2/NuRD: multiple complexes for many purposes. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2004;1677:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Brunak S, Engelbrecht J, Knudsen S. Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1991;220:49–65. - PubMed
-
- Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science. 1996;272:877–880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA85786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA089810/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054430/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085786-07/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085786-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA026192/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RR22220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082396/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM62427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI54430/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA085786-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA89810/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

