Cytokine signaling modules in inflammatory responses
- PMID: 18400190
- PMCID: PMC2782488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.002
Cytokine signaling modules in inflammatory responses
Abstract
Cytokine signaling via a restricted number of Jak-Stat pathways positively and negatively regulates all cell types involved in the initiation, propagation, and resolution of inflammation. Here, we focus on Jak-Stat signaling in three major cell types involved in inflammatory responses: T cells, neutrophils, and macrophages. We summarize how the Jak-Stat pathways in these cells are negatively regulated by the Suppressor of cytokine signaling (Socs) proteins. We emphasize that common Jak-Stat-Socs signaling modules can have diverse developmental, pro- and anti-inflammatory outcomes depending on the cytokine receptor activated and which genes are accessible at a given time in a cell's life. Because multiple components of Jak-Stat-Socs pathways are mutated or closely associated with human inflammatory diseases, and cytokine-based therapies are increasingly deployed to treat inflammation, understanding cytokine signaling will continue to advance our ability to manipulate chronic and acute inflammatory diseases.
Figures

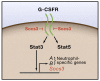
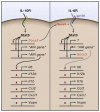

Similar articles
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and JAK/STAT pathways: regulation of T-cell inflammation by SOCS1 and SOCS3.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 May;31(5):980-5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207464. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21508344 Review.
-
Potential Natural Biomolecules Targeting JAK/STAT/SOCS Signaling in the Management of Atopic Dermatitis.Molecules. 2022 Jul 21;27(14):4660. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144660. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpreting mixed signals: the cell's cytokine conundrum.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Oct;23(5):632-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.07.013. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21852079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jak/STAT/SOCS signaling circuits and associated cytokine-mediated inflammation and hypertrophy in the heart.Shock. 2006 Sep;26(3):226-34. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000226341.32786.b9. Shock. 2006. PMID: 16912647 Review.
-
Epigenetic silencing of SOCS5 potentiates JAK-STAT signaling and progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jun;110(6):1931-1946. doi: 10.1111/cas.14021. Epub 2019 May 3. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30974024 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Altered responses to homeostatic cytokines in patients with idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055570. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383227 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-inflammatory effects of a methanolic extract from Radix Isatidis in murine macrophages and mice.Inflammation. 2010 Apr;33(2):110-8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9164-9. Inflammation. 2010. PMID: 19888641
-
IL-17A is proatherogenic in high-fat diet-induced and Chlamydia pneumoniae infection-accelerated atherosclerosis in mice.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 1;185(9):5619-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001879. Epub 2010 Oct 8. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20935201 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive response of CNS glial cells in oro-facial pain associated with injury, infection and inflammation.Mol Pain. 2010 Nov 10;6:79. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-79. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 21067602 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Cell. 2009 Feb 3;15(2):114-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.018. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19185846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander WS, Hilton DJ. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:503–529. - PubMed
-
- Alexander WS, Starr R, Fenner JE, Scott CL, Handman E, Sprigg NS, Corbin JE, Cornish AL, Darwiche R, Owczarek CM, et al. SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon gamma signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions of this cytokine. Cell. 1999;98:597–608. - PubMed
-
- Baetz A, Frey M, Heeg K, Dalpke AH. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins indirectly regulate toll-like receptor signaling in innate immune cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:54708–54715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

