Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling causes defects in postnatal cartilage development
- PMID: 18397998
- PMCID: PMC2636704
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.020362
Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling causes defects in postnatal cartilage development
Abstract
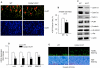
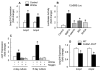
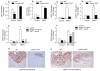
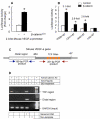
The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway is essential for normal skeletal development because conditional gain or loss of function of beta-catenin in cartilage results in embryonic or early postnatal death. To address the role of beta-catenin in postnatal skeletal growth and development, Col2a1-ICAT transgenic mice were generated. Mice were viable and had normal size at birth, but became progressively runted. Transgene expression was limited to the chondrocytes in the growth plate and articular cartilages and was associated with decreased beta-catenin signaling. Col2a1-ICAT transgenic mice showed reduced chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, and an increase in chondrocyte apoptosis, leading to decreased widths of the proliferating and hypertrophic zones, delayed formation of the secondary ossification center, and reduced skeletal growth. Isolated primary Col2a1-ICAT transgenic chondrocytes showed reduced expression of chondrocyte genes associated with maturation, and demonstrated that VEGF gene expression requires cooperative interactions between BMP2 and beta-catenin signaling. Altogether the findings confirm a crucial role for Wnt/beta-catenin in postnatal growth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chondrocyte-specific inhibition of β-catenin signaling leads to dysplasia of the caudal vertebrae in mice.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Nov 15;38(24):2079-84. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000435024.57940.8d. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 24026150 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of beta-catenin signaling in articular chondrocytes results in articular cartilage destruction.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Jul;58(7):2053-64. doi: 10.1002/art.23614. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18576323 Free PMC article.
-
Cartilage-specific β-catenin signaling regulates chondrocyte maturation, generation of ossification centers, and perichondrial bone formation during skeletal development.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Aug;27(8):1680-94. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1639. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22508079 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on biology and pathology of HIF-1α/-2α, TGFβ/BMP, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF-κB pathways in osteoarthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(22):3293-312. doi: 10.2174/1381612811209023293. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22646092 Review.
-
Wnt signaling in chondroprogenitors during long bone development and growth.Bone. 2020 Aug;137:115368. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115368. Epub 2020 May 4. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32380258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental Regulation of the Growth Plate and Cranial Synchondrosis.J Dent Res. 2016 Oct;95(11):1221-9. doi: 10.1177/0022034516651823. Epub 2016 Jun 1. J Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 27250655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Wnt signaling cascade in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and related promising treatment strategies.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 2;13:954454. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.954454. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36117702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP-2 modulates beta-catenin signaling through stimulation of Lrp5 expression and inhibition of beta-TrCP expression in osteoblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Nov 1;108(4):896-905. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22319. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19795382 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 7 (Hdac7) suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and β-catenin activity during endochondral ossification.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 2;290(1):118-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.596247. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25389289 Free PMC article.
-
Role and Mechanisms of Actions of Thyroid Hormone on the Skeletal Development.Bone Res. 2013 Jun 28;1(2):146-61. doi: 10.4248/BR201302004. eCollection 2013 Jun. Bone Res. 2013. PMID: 26273499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brault V, Moore R, Kutsch S, Ishibashi M, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP, Sommer L, Boussadia O, Kemler R. Inactivation of the beta-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development. 2001;128:1253–1264. - PubMed
-
- Daniels DL, Weis WI. ICAT inhibits beta-catenin binding to Tcf/Lef-family transcription factors and the general coactivator p300 using independent structural modules. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:573–584. - PubMed
-
- DasGupta R, Fuchs E. Multiple roles for activated LEF/TCF transcription complexes during hair follicle development and differentiation. Development. 1999;126:4557–4568. - PubMed
-
- Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev. Cell. 2005;8:739–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR051189-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR 053717/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054465-01/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR 038945/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR038945/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051189/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051189-04/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AR052411-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR053717/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AR052411-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AR052411/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054465-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051189-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR 054465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

