RNAIII-inhibiting peptide enhances healing of wounds infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 18391046
- PMCID: PMC2415788
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01340-07
RNAIII-inhibiting peptide enhances healing of wounds infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
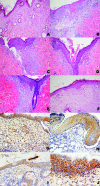
Quorum sensing is a mechanism through which a bacterial population receives input from neighboring cells and elicits an appropriate response to enable survival within the host. Inhibiting quorum sensing by RNAIII-inhibiting peptide (RIP) has been demonstrated as a very effective mode of prevention and therapy for device-associated staphylococcal infections and was tested here for healing of wounds that are otherwise resistant to conventional antibiotics. Wounds, established through the panniculus carnosus of BALB/c mice, were inoculated with 5 x 10(7) CFU of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mice were treated with Allevyn, RIP-soaked Allevyn (containing 20 microg RIP), daily intraperitoneal teicoplanin (7 mg/kg of body weight), Allevyn and teicoplanin, and RIP-soaked Allevyn and daily intraperitoneal teicoplanin. The main outcome measures were quantitative bacterial culture and histological examination with assessment of microvessel density and of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in tissue sections. Treatment with RIP-soaked Allevyn together with teicoplanin injection greatly reduced the bacterial load to 13 CFU/g (control untreated animals had 10(8) CFU/g bacteria). All other treatments were also significantly effective but only reduced the bacterial load to about 10(3) CFU/ml. Histological examination indicated that only treatment with RIP-soaked Allevyn with teicoplanin injection restored epithelial, granulation, and collagen scores, as well as microvessel density and VEGF expression, to the levels found with uninfected mice. In conclusion, we observed that RIP may be useful for the management of infected wounds and that it could represent an exciting and future alternative to the conventional antibiotics, at present considered the gold-standard treatments for methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections.
Figures
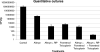
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the Quorum Sensing Inhibitor FS10 Alone and in Combination with Tigecycline in an Animal Model of Staphylococcal Infected Wound.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 2;11(6):e0151956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151956. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27253706 Free PMC article.
-
Temporin A is effective in MRSA-infected wounds through bactericidal activity and acceleration of wound repair in a murine model.Peptides. 2008 Apr;29(4):520-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.12.011. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Peptides. 2008. PMID: 18255189
-
Comparative efficacy of topical versus systemic teicoplanin in experimental model of wound infections.J Surg Res. 2008 Jan;144(1):74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.02.051. Epub 2007 Jun 14. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 17574587
-
RNAIII Inhibiting Peptide (RIP) and Derivatives as Potential Tools for the Treatment of S. aureus Biofilm Infections.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(24):2068-2079. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666181022120711. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30345922 Review.
-
Suppression of biofilm related, device-associated infections by staphylococcal quorum sensing inhibitors.Int J Artif Organs. 2008 Sep;31(9):761-70. doi: 10.1177/039139880803100903. Int J Artif Organs. 2008. PMID: 18924087 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of the Quorum Sensing Inhibitor FS10 Alone and in Combination with Tigecycline in an Animal Model of Staphylococcal Infected Wound.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 2;11(6):e0151956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151956. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27253706 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of the immune response by bacteriophages alters methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 19;12(1):15656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19922-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36123529 Free PMC article.
-
MRSA and Skin Infections in Psoriatic Patients: Therapeutic Options and New Perspectives.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;11(11):1504. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111504. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358159 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal Biofilm on the Surface of Catheters: Electron Microscopy Evaluation of the Inhibition of Biofilm Growth by RNAIII Inhibiting Peptide.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jul 20;10(7):879. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070879. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356800 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm-related infections: bridging the gap between clinical management and fundamental aspects of recalcitrance toward antibiotics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Sep;78(3):510-43. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00013-14. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25184564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyama, H., H. Kanzaki, Y. Abe, J. Tada, and J. Arata. 1994. Staphylococcus aureus infection on experimental croton oil-inflamed skin in mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 8:1-10. - PubMed
-
- Anguita-Alonso, P., A. Giacometti, O. Cirioni, R. Ghiselli, F. Orlando, V. Saba, G. Scalise, M. Sevo, M. Tuzova, R. Patel, and N. Balaban. 2007. RNAIII-inhibiting-peptide-loaded polymethylmethacrylate prevents in vivo Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:2594-2596. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., A. Giacometti, O. Cirioni, Y. Gov, R. Ghiselli, F. Moccheggiani, C. Viticchi, M. S. Del Prete, V. Saba, G. Scalise, and G. Dell'Acqua. 2003. Use of the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAIII-inhibiting peptide to prevent biofilm formation in vivo by drug-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Infect. Dis. 187:625-630. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., T. Goldkorn, Y. Gov, M. Hirshberg, N. Koyfman, H. R. Matthews, R. T. Nhan, B. Singh, and O. Uziel. 2001. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII activating protein (TRAP). J. Biol. Chem. 276:2658-2667. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., T. Goldkorn, R. T. Nhan, L. B. Dang, S. Scott, R. M. Ridgley, A. Rasooly, S. C. Wright, J. W. Larrick, R. Rasooly, and J. R. Carlson. 1998. Autoinducer of virulence as a target for vaccine and therapy against Staphylococcus aureus. Science 280:438-440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

