Hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate mediates calcium-induced inactivation of TRPV6 channels
- PMID: 18390907
- PMCID: PMC2397461
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M704224200
Hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate mediates calcium-induced inactivation of TRPV6 channels
Abstract
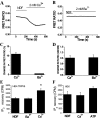
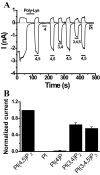
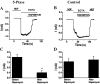
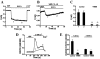
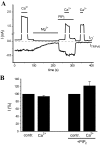
TRPV6 is a member of the transient receptor potential superfamily of ion channels that facilitates Ca(2+) absorption in the intestines. These channels display high selectivity for Ca(2+), but in the absence of divalent cations they also conduct monovalent ions. TRPV6 channels have been shown to be inactivated by increased cytoplasmic Ca(2+) concentrations. Here we studied the mechanism of this Ca(2+)-induced inactivation. Monovalent currents through TRPV6 substantially decreased after a 40-s application of Ca(2+), but not Ba(2+). We also show that Ca(2+), but not Ba(2+), influx via TRPV6 induces depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P(2) or PIP(2)) and the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Dialysis of DiC(8) PI(4,5)P(2) through the patch pipette inhibited Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation of TRPV6 currents in whole-cell patch clamp experiments. PI(4,5)P(2) also activated TRPV6 currents in excised patches. PI(4)P, the precursor of PI(4,5)P(2), neither activated TRPV6 in excised patches nor had any effect on Ca(2+)-induced inactivation in whole-cell experiments. Conversion of PI(4,5)P(2) to PI(4)P by a rapamycin-inducible PI(4,5)P(2) 5-phosphatase inhibited TRPV6 currents in whole-cell experiments. Inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 4 kinases with wortmannin decreased TRPV6 currents and Ca(2+) entry into TRPV6-expressing cells. We propose that Ca(2+) influx through TRPV6 activates phospholipase C and the resulting depletion of PI(4,5)P(2) contributes to the inactivation of TRPV6.
Figures
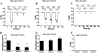
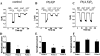
Similar articles
-
Phospholipase C-mediated regulation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels: implications in active intestinal Ca2+ transport.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;75(3):608-16. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.052449. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19073818 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between calmodulin and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in Ca2+-induced inactivation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 channels.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 22;288(8):5278-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409482. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23300090 Free PMC article.
-
The recombinant human TRPV6 channel functions as Ca2+ sensor in human embryonic kidney and rat basophilic leukemia cells.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 27;277(39):36656-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202822200. Epub 2002 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12138163
-
Structure and function of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6.J Physiol. 2021 May;599(10):2673-2697. doi: 10.1113/JP279024. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32073143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Store-Independent Orai Channels Regulated by STIM.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 11. PMID: 30299650 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of transient receptor potential cation channels in Ca2+ signaling.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Oct;2(10):a003962. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003962. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20861159 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and gating mechanism of the transient receptor potential channel TRPV3.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018 Sep;25(9):805-813. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0108-7. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30127359 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanisms of TRPV6 inhibition by ruthenium red and econazole.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 1;12(1):6284. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26608-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34725357 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ Regulation of TRP Ion Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 23;19(4):1256. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041256. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29690581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Interactions of a Ciliary Membrane TRP Channel: Simulation and Structural Studies of Polycystin-2.Structure. 2020 Feb 4;28(2):169-184.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Structure. 2020. PMID: 31806353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Montell, C. (2005) Sci. STKE 2005 re3. - PubMed
-
- Nilius, B., Owsianik, G., Voets, T., and Peters, J. A. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87 165–217 - PubMed
-
- Clapham, D. E. (2003) Nature 426 517–524 - PubMed
-
- Hoenderop, J. G., Nilius, B., and Bindels, R. J. (2005) Physiol. Rev. 85 373–422 - PubMed
-
- Vennekens, R., Voets, T., Bindels, R. J., Droogmans, G., and Nilius, B. (2002) Cell Calcium 31 253–264 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

