miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region
- PMID: 18367714
- PMCID: PMC2327368
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.972008
miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region
Abstract
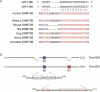
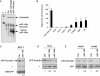
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNA molecules of 20-24 nucleotides that regulate gene expression. In animals, miRNAs form imperfect interactions with sequences in the 3' Untranslated region (3'UTR) of mRNAs, causing translational inhibition and mRNA decay. In contrast, plant miRNAs mostly associate with protein coding regions. Here we show that human miR-148 represses DNA methyltransferase 3b (Dnmt3b) gene expression through a region in its coding sequence. This region is evolutionary conserved and present in the Dnmt3b splice variants Dnmt3b1, Dnmt3b2, and Dnmt3b4, but not in the abundantly expressed Dnmt3b3. Whereas overexpression of miR-148 results in decreased DNMT3b1 expression, short-hairpin RNA-mediated miR-148 repression leads to an increase in DNMT3b1 expression. Interestingly, mutating the putative miR-148 target site in Dnmt3b1 abolishes regulation by miR-148. Moreover, endogenous Dnmt3b3 mRNA, which lacks the putative miR-148 target site, is resistant to miR-148-mediated regulation. Thus, our results demonstrate that the coding sequence of Dnmt3b mediates regulation by the miR-148 family. More generally, we provide evidence that coding regions of human genes can be targeted by miRNAs, and that such a mechanism might play a role in determining the relative abundance of different splice variants.
Figures
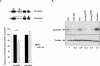

Similar articles
-
Target identification of microRNAs expressed highly in human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Apr 15;106(6):1020-30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22084. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19229866
-
miR-125b targets DNMT3b and mediates p53 DNA methylation involving in the vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation induced by homocysteine.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Sep 10;347(1):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27426728
-
Wnt signalling mediates miR-133a nuclear re-localization for the transcriptional control of Dnmt3b in cardiac cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 27;9(1):9320. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45818-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31249372 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Positive and negative modulation of viral and cellular mRNAs by liver-specific microRNA miR-122.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:369-76. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.022. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381319 Review.
Cited by
-
Sounds of silence: synonymous nucleotides as a key to biological regulation and complexity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(4):2073-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1205. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23293005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-494 is a master epigenetic regulator of multiple invasion-suppressor microRNAs by targeting ten eleven translocation 1 in invasive human hepatocellular carcinoma tumors.Hepatology. 2015 Aug;62(2):466-80. doi: 10.1002/hep.27816. Epub 2015 May 6. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25820676 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive miRNA sequence analysis reveals survival differences in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.Genome Biol. 2015 Jan 29;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0568-y. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 25723320 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-148a in hepatitis B associated hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035331. Epub 2012 Apr 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22496917 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-148a inhibits angiogenesis by targeting ERBB3.J Biomed Res. 2011 May;25(3):170-7. doi: 10.1016/S1674-8301(11)60022-5. J Biomed Res. 2011. PMID: 23554686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agami, R., Bernards, R. Distinct initiation and maintenance mechanisms cooperate to induce G1 cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. Cell. 2000;102:55–66. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T.R., Bernards, R., Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
