Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 in blood, plasma, and serum
- PMID: 18367583
- PMCID: PMC2446627
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00385-07
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 in blood, plasma, and serum
Abstract
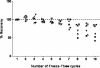
Microscopy, the gold standard for the detection and quantification of malaria parasites in blood, is in many aspects deficient for this purpose. The method is poorly reproducible and can be inaccurate because Plasmodium falciparum parasites sequester for a portion of each asexual cycle. Due to these deficiencies, biomarkers such as P. falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP2) are increasingly being used. In this study, we evaluated the use of a commercial PfHRP2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit with some procedural modifications. We determined the linear range of the assay, including the lower limits of detection and quantitation, using recombinant PfHRP2 (rPfHRP2). In 10 repeat experiments, the linear range of optical densities (ODs) at 450 to 650 nm was from 0.05 +/- 0.002 to 2.28 +/- 0.042, corresponding to 3.91 to 250 ng/ml of rPfHRP2. The coefficient of variation (CV) at each target concentration ranged from 1.93 to 8.07%. Using cultured parasites, we confirmed the linear range of ODs as well as the association between the PfHRP2 ELISA results and the microscopic parasite densities. For whole-blood samples spiked with cultured, washed, ring-stage-infected red blood cells (iRBCs), the linear range was 11.7 to 750 iRBCs/microl, with CVs of 0.29 to 7.56%. The same spiked samples evaluated by microscopists had similar sensitivities, but the CVs were unacceptably high (20.7 to 161.6%). Stock rPfHRP2 was stable through four freeze-thaw cycles (P < 0.05; paired t test). When different patient sample types at different concentrations within the linear range of the assay are compared, the recoveries of PfHRP2 from blood and serum were within +/-20%, whereas the recoveries from plasma ranged between +35 and -41%. We conclude that PfHRP2 ELISA using whole-blood and serum samples is a suitable adjunct to microscopy and could ultimately benefit malaria intervention trials.
Figures
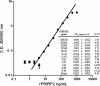

 , 15.1; ◭, 31.3; ⬘, 62.5; ⬒, 125.0; ◓, 250.0.
, 15.1; ◭, 31.3; ⬘, 62.5; ⬒, 125.0; ◓, 250.0.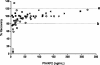
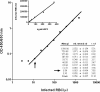
 ), and serum (▪), assessed at different dilutions, and were taken from patients with low, medium, and high levels of PfHRP2. Analyte recovery was determined by comparing observed values with expected values. The precision of the assay was within the acceptable ±20% range (area between the dashed lines marked “a” and “b”) between the lower LOQ (3.91 ng/ml; arrow) and the upper LOQ (250 ng/ml) for serum and whole-blood samples. Plasma samples had higher CVs (+35 to −41%) at PfHRP2 concentrations of ≤25 ng/ml.
), and serum (▪), assessed at different dilutions, and were taken from patients with low, medium, and high levels of PfHRP2. Analyte recovery was determined by comparing observed values with expected values. The precision of the assay was within the acceptable ±20% range (area between the dashed lines marked “a” and “b”) between the lower LOQ (3.91 ng/ml; arrow) and the upper LOQ (250 ng/ml) for serum and whole-blood samples. Plasma samples had higher CVs (+35 to −41%) at PfHRP2 concentrations of ≤25 ng/ml.Similar articles
-
Production and characterization of specific monoclonal antibodies binding the Plasmodium falciparum diagnostic biomarker, histidine-rich protein 2.Malar J. 2014 Jul 18;13:277. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-277. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 25037150 Free PMC article.
-
A new highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 in whole blood.Malar J. 2018 Nov 1;17(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2545-5. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 30384849 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic potential of monoclonal antibodies developed against C-terminal polypeptide of P. falciparum Histidine Rich Protein2 (PfHRP2) in malaria infected patients from India.Pathog Glob Health. 2017 Sep;111(6):297-305. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2017.1358846. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Pathog Glob Health. 2017. PMID: 28777043 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and deletion of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 and 3: a threat to diagnosis of P. falciparum malaria.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 May;25(5):580-585. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 30267926 Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum parasites lacking histidine-rich protein 2 and 3: a review and recommendations for accurate reporting.Malar J. 2014 Jul 22;13:283. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-283. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 25052298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid Redox Probe-Free Plastic Antibody Development for Malaria Biomarker Recognition.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 15;9(30):33130-33139. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04543. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39100316 Free PMC article.
-
How well do malaria tests correlate with disease severity? Comparison of parasite density in children with mild and severe malaria.Malariaworld J. 2014 Jun 26;5:7. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.10887755. eCollection 2014. Malariaworld J. 2014. PMID: 38764802 Free PMC article.
-
Post-treatment haemolysis is common following oral artemisinin combination therapy of uncomplicated malaria in travellers.J Travel Med. 2023 May 18;30(3):taad001. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taad001. J Travel Med. 2023. PMID: 36611010 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed micronutrient, inflammation, and malarial antigenemia assessment using a plasma fractionation device.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 21;17(11):e0277835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277835. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36409692 Free PMC article.
-
Malaria diagnostic update: From conventional to advanced method.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24314. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24314. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35247002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amexo, M., R. Tolhurst, G. Barnish, and I. Bates. 2004. Malaria misdiagnosis: effects on the poor and vulnerable. Lancet 364:1896-1898. - PubMed
-
- Bacon, D. J., C. Latour, C. Lucas, O. Colina, P. Ringwald, and S. Picot. 2007. Comparison of a SYBR green I-based assay with a histidine-rich protein II enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for in vitro antimalarial drug efficacy testing and application to clinical isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:1172-1178. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, J., J. McCarthy, M. Gatton, D. E. Kyle, V. Belizario, J. Luchavez, D. Bell, and Q. Cheng. 2005. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP2) and its effect on the performance of PfHRP2-based rapid diagnostic tests. J. Infect. Dis. 192:870-877. - PubMed
-
- Bland, J. M., and D. G. Altman. 1986. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet i:307-310. - PubMed
-
- Chiodini, P. L., K. Bowers, P. Jorgensen, J. W. Barnwell, K. K. Grady, J. Luchavez, A. H. Moody, A. Cenizal, and D. Bell. 2007. The heat stability of Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase-based and histidine-rich protein 2-based malaria rapid diagnostic tests. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 101:331-337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

