Substituents on etoposide that interact with human topoisomerase IIalpha in the binary enzyme-drug complex: contributions to etoposide binding and activity
- PMID: 18355043
- PMCID: PMC2737519
- DOI: 10.1021/bi702019z
Substituents on etoposide that interact with human topoisomerase IIalpha in the binary enzyme-drug complex: contributions to etoposide binding and activity
Abstract
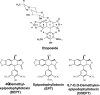
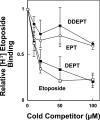
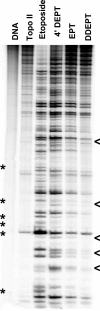
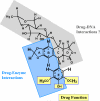
Etoposide is a widely prescribed anticancer agent that stabilizes topoisomerase II-mediated DNA strand breaks. The drug contains a polycyclic ring system (rings A-D), a glycosidic moiety at C4, and a pendant ring (E-ring) at C1. A recent study that focused on yeast topoisomerase II demonstrated that the H15 geminal protons of the etoposide A-ring, the H5 and H8 protons of the B-ring, and the H2', H6', 3'-methoxyl, and 5'-methoxyl protons of the E-ring contact topoisomerase II in the binary enzyme-drug complex [ Wilstermann et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46, 8217-8225 ]. No interactions with the C4 sugar were observed. The present study used DNA cleavage assays, saturation transfer difference [ (1)H] NMR spectroscopy, and enzyme-drug binding studies to further define interactions between etoposide and human topoisomerase IIalpha. Etoposide and three derivatives that lacked the C4 sugar were analyzed. Except for the sugar, 4'-demethyl epipodophyllotoxin is identical to etoposide, epipodophyllotoxin contains a 4'-methoxyl group on the E-ring, and 6,7- O, O-demethylenepipodophyllotoxin replaces the A-ring with a diol. Results suggest that etoposide-topoisomerase IIalpha binding is driven by interactions with the A- and B-rings and potentially by stacking interactions with the E-ring. We propose that the E-ring pocket on the enzyme is confined, because the addition of bulk to this ring adversely affects drug function. The A- and E-rings do not appear to contact DNA in the enzyme-drug-DNA complex. Conversely, the sugar moiety subtly alters DNA interactions. The identification of etoposide substituents that contact topoisomerase IIalpha in the binary complex has predictive value for drug behavior in the enzyme-etoposide-DNA complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contributions of the D-Ring to the activity of etoposide against human topoisomerase IIα: potential interactions with DNA in the ternary enzyme--drug--DNA complex.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 7;50(22):5058-66. doi: 10.1021/bi200531q. Epub 2011 May 13. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21548574 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase II - drug interaction domains: identification of substituents on etoposide that interact with the enzyme.Biochemistry. 2007 Jul 17;46(28):8217-25. doi: 10.1021/bi700272u. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17580961 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between the etoposide derivative F14512 and human type II topoisomerases: implications for the C4 spermine moiety in promoting enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage.Biochemistry. 2011 Apr 19;50(15):3240-9. doi: 10.1021/bi200094z. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21413765 Free PMC article.
-
DNA topoisomerase II as the target for the anticancer drug TOP-53: mechanistic basis for drug action.Biochemistry. 2001 Jan 23;40(3):712-8. doi: 10.1021/bi0021838. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11170388
-
Pharmaceutical and pharmacological approaches for bioavailability enhancement of etoposide.J Biosci. 2014 Mar;39(1):139-44. doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9399-3. J Biosci. 2014. PMID: 24499798 Review.
Cited by
-
Etoposide quinone is a redox-dependent topoisomerase II poison.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 28;50(25):5660-7. doi: 10.1021/bi200438m. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21595477 Free PMC article.
-
Neoamphimedine circumvents metnase-enhanced DNA topoisomerase IIα activity through ATP-competitive inhibition.Mar Drugs. 2011;9(11):2397-2408. doi: 10.3390/md9112397. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Mar Drugs. 2011. PMID: 22163192 Free PMC article.
-
Amsacrine as a topoisomerase II poison: importance of drug-DNA interactions.Biochemistry. 2012 Feb 28;51(8):1730-9. doi: 10.1021/bi201159b. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22304499 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of quinolone CP-115,955 against bacterial and human type II topoisomerases is mediated by different interactions.Biochemistry. 2015 Feb 10;54(5):1278-86. doi: 10.1021/bi501073v. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25586498 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase II Poisons: Converting Essential Enzymes into Molecular Scissors.Biochemistry. 2021 Jun 1;60(21):1630-1641. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00240. Epub 2021 May 19. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 34008964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hande KR. Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur. J. Cancer. 1998;34:1514–1521. - PubMed
-
- Hande KR. Clinical applications of anticancer drugs targeted to topoisomerase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1400:173–184. - PubMed
-
- Holden JA. DNA topoisomerases as anticancer drug targets: from the laboratory to the clinic. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents. 2001;1:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin EL, Osheroff N. Etoposide, topoisomerase II and cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Canc. Agents. 2005;5:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss JL, Liu YX, Hsiung Y. A temperature sensitive topoisomerase II allele confers temperature dependent drug resistance on amsacrine and etoposide: a genetic system for determining the targets of topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer Research. 1993;53:89–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

