Chromatin dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the mouse germ line
- PMID: 18354397
- PMCID: PMC3847605
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06714
Chromatin dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the mouse germ line
Abstract
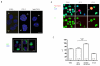
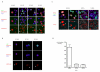
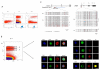
A unique feature of the germ cell lineage is the generation of totipotency. A critical event in this context is DNA demethylation and the erasure of parental imprints in mouse primordial germ cells (PGCs) on embryonic day 11.5 (E11.5) after they enter into the developing gonads. Little is yet known about the mechanism involved, except that it is apparently an active process. We have examined the associated changes in the chromatin to gain further insights into this reprogramming event. Here we show that the chromatin changes occur in two steps. The first changes in nascent PGCs at E8.5 establish a distinctive chromatin signature that is reminiscent of pluripotency. Next, when PGCs are residing in the gonads, major changes occur in nuclear architecture accompanied by an extensive erasure of several histone modifications and exchange of histone variants. Furthermore, the histone chaperones HIRA and NAP-1 (NAP111), which are implicated in histone exchange, accumulate in PGC nuclei undergoing reprogramming. We therefore suggest that the mechanism of histone replacement is critical for these chromatin rearrangements to occur. The marked chromatin changes are intimately linked with genome-wide DNA demethylation. On the basis of the timing of the observed events, we propose that if DNA demethylation entails a DNA repair-based mechanism, the evident histone replacement would represent a repair-induced response event rather than being a prerequisite.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Epigenetic Changes During Human Gonadal Primordial Germ Cells Reprogramming.Stem Cells. 2016 Sep;34(9):2418-28. doi: 10.1002/stem.2422. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 27300161 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide reprogramming in the mouse germ line entails the base excision repair pathway.Science. 2010 Jul 2;329(5987):78-82. doi: 10.1126/science.1187945. Science. 2010. PMID: 20595612 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular dynamics associated with the genome-wide epigenetic reprogramming in migrating primordial germ cells in mice.Development. 2007 Jul;134(14):2627-38. doi: 10.1242/dev.005611. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Development. 2007. PMID: 17567665
-
A current view of the epigenome in mouse primordial germ cells.Mol Reprod Dev. 2014 Feb;81(2):160-70. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22214. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Mol Reprod Dev. 2014. PMID: 23868517 Review.
-
Epigenetic profiles in primordial germ cells: global modulation and fine tuning of the epigenome for acquisition of totipotency.Dev Growth Differ. 2010 Aug;52(6):517-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2010.01190.x. Dev Growth Differ. 2010. PMID: 20646024 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation shapes the Polycomb landscape during the exit from naive pluripotency.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 24. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01405-4. Online ahead of print. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39448850
-
Efficient genetic modification and germ-line transmission of primordial germ cells using piggyBac and Tol2 transposons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 5;109(23):E1466-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118715109. Epub 2012 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22586100 Free PMC article.
-
CpG methylation recruits sequence specific transcription factors essential for tissue specific gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):763-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.014. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22387149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication-coupled passive DNA demethylation for the erasure of genome imprints in mice.EMBO J. 2013 Feb 6;32(3):340-53. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.331. Epub 2012 Dec 14. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23241950 Free PMC article.
-
The germ cell determinant Blimp1 is not required for derivation of pluripotent stem cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2012 Jul 6;11(1):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.023. Cell Stem Cell. 2012. PMID: 22770244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hajkova P, et al. Epigenetic reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mech Dev. 2002;117:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Lee J, et al. Erasing genomic imprinting memory in mouse clone embryos produced from day 11.5 primordial germ cells. Development. 2002;129:1807–17. - PubMed
-
- Ohinata Y, et al. Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature. 2005;436:207–13. - PubMed
-
- Ancelin K, et al. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:623–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

