Activation of ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage bypass is mediated by replication protein a
- PMID: 18342608
- PMCID: PMC2507760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.016
Activation of ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage bypass is mediated by replication protein a
Abstract
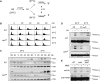
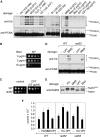
Replicative DNA damage bypass, mediated by the ubiquitylation of the sliding clamp protein PCNA, facilitates the survival of a cell in the presence of genotoxic agents, but it can also promote genomic instability by damage-induced mutagenesis. We show here that PCNA ubiquitylation in budding yeast is activated independently of the replication-dependent S phase checkpoint but by similar conditions involving the accumulation of single-stranded DNA at stalled replication intermediates. The ssDNA-binding replication protein A (RPA), an essential complex involved in most DNA transactions, is required for damage-induced PCNA ubiquitylation. We found that RPA directly interacts with the ubiquitin ligase responsible for the modification of PCNA, Rad18, both in yeast and in mammalian cells. Association of the ligase with chromatin is detected where RPA is most abundant, and purified RPA can recruit Rad18 to ssDNA in vitro. Our results therefore implicate the RPA complex in the activation of DNA damage tolerance.
Figures



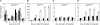

Similar articles
-
Cooperation of replication protein A with the ubiquitin ligase Rad18 in DNA damage bypass.Cell Cycle. 2008 Dec;7(23):3629-33. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.23.7166. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19029798
-
Replication protein A dynamically regulates monoubiquitination of proliferating cell nuclear antigen.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5157-5168. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005297. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30700555 Free PMC article.
-
PCNA Monoubiquitination Is Regulated by Diffusion of Rad6/Rad18 Complexes along RPA Filaments.Biochemistry. 2020 Dec 15;59(49):4694-4702. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00849. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 33242956 Free PMC article.
-
Error-free DNA-damage tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015 Apr-Jun;764:43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 26041265 Review.
-
DNA-damage tolerance through PCNA ubiquitination and sumoylation.Biochem J. 2020 Jul 31;477(14):2655-2677. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190579. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32726436 Review.
Cited by
-
Human DNA helicase B (HDHB) binds to replication protein A and facilitates cellular recovery from replication stress.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6469-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.324582. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22194613 Free PMC article.
-
ATAD5 regulates the lifespan of DNA replication factories by modulating PCNA level on the chromatin.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jan 7;200(1):31-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201206084. Epub 2012 Dec 31. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23277426 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage bypass is separable from genome replication.Nature. 2010 Jun 17;465(7300):951-5. doi: 10.1038/nature09097. Epub 2010 May 9. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20453836 Free PMC article.
-
Avidity-based biosensors for ubiquitylated PCNA reveal choreography of DNA damage bypass.Sci Adv. 2023 Sep 8;9(36):eadf3041. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf3041. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37672592 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse roles of RAD18 and Y-family DNA polymerases in tumorigenesis.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(7):833-843. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1456296. Epub 2018 May 8. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29683380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Branzei D., Foiani M. The DNA damage response during DNA replication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005;17:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Chang D.J., Lupardus P.J., Cimprich K.A. Monoubiquitination of proliferating cell nuclear antigen induced by stalled replication requires uncoupling of DNA polymerase and mini-chromosome maintenance helicase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:32081–32088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

