Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder
- PMID: 18317468
- PMCID: PMC3777816
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002151
Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder
Abstract
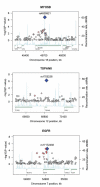
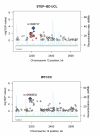
We performed a genome-wide association scan in 1461 patients with bipolar (BP) 1 disorder, 2008 controls drawn from the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program for Bipolar Disorder and the University College London sample collections with successful genotyping for 372,193 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Our strongest single SNP results are found in myosin5B (MYO5B; P=1.66 x 10(-7)) and tetraspanin-8 (TSPAN8; P=6.11 x 10(-7)). Haplotype analysis further supported single SNP results highlighting MYO5B, TSPAN8 and the epidermal growth factor receptor (MYO5B; P=2.04 x 10(-8), TSPAN8; P=7.57 x 10(-7) and EGFR; P=8.36 x 10(-8)). For replication, we genotyped 304 SNPs in family-based NIMH samples (n=409 trios) and University of Edinburgh case-control samples (n=365 cases, 351 controls) that did not provide independent replication after correction for multiple testing. A comparison of our strongest associations with the genome-wide scan of 1868 patients with BP disorder and 2938 controls who completed the scan as part of the Wellcome Trust Case-Control Consortium indicates concordant signals for SNPs within the voltage-dependent calcium channel, L-type, alpha 1C subunit (CACNA1C) gene. Given the heritability of BP disorder, the lack of agreement between studies emphasizes that susceptibility alleles are likely to be modest in effect size and require even larger samples for detection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional variants of TSPAN8 are associated with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010 Jun 5;153B(4):967-72. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31057. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 20052686
-
Suggestive evidence for association between L-type voltage-gated calcium channel (CACNA1C) gene haplotypes and bipolar disorder in Latinos: a family-based association study.Bipolar Disord. 2013 Mar;15(2):206-14. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12041. Bipolar Disord. 2013. PMID: 23437964 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin Vb gene is associated with schizophrenia in Chinese Han population.Psychiatry Res. 2013 May 15;207(1-2):13-8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2013.02.026. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Psychiatry Res. 2013. PMID: 23561489
-
Extracting a needle from a haystack: reanalysis of whole genome data reveals a readily translatable finding.Psychol Med. 2009 Aug;39(8):1231-5. doi: 10.1017/S0033291708005084. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Psychol Med. 2009. PMID: 19215628 Review.
-
Comprehensive field synopsis and systematic meta-analyses of genetic association studies in cutaneous melanoma.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Aug 17;103(16):1227-35. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr219. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21693730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cadherins and catenins in dendrite and synapse morphogenesis.Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(3):202-13. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.994919. Cell Adh Migr. 2015. PMID: 25914083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential serum levels of CACNA1C, circadian rhythm and stress response molecules in subjects with bipolar disorder: Associations with genetic and clinical factors.J Affect Disord. 2024 Dec 15;367:148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.08.238. Epub 2024 Sep 2. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 39233237
-
Seasonality shows evidence for polygenic architecture and genetic correlation with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.J Clin Psychiatry. 2015 Feb;76(2):128-34. doi: 10.4088/JCP.14m08981. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25562672 Free PMC article.
-
CACNA1C risk variant is associated with increased amygdala volume.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016 Apr;266(3):269-75. doi: 10.1007/s00406-015-0609-x. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26048451
-
Frontotemporal White Matter in Adolescents with, and at-Risk for, Bipolar Disorder.J Clin Med. 2014 Mar 10;3(1):233-54. doi: 10.3390/jcm3010233. J Clin Med. 2014. PMID: 26237259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH062137/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G9623693N/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MH63420/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067288/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH067288/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063445/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 MH002810/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089905/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD060726/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH062137/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059534/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0500791/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH60068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG005827/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063420/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01MH80001/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH063445/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 066717/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

