The Caenorhabditis elegans nephrocystins act as global modifiers of cilium structure
- PMID: 18316409
- PMCID: PMC2265406
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200707090
The Caenorhabditis elegans nephrocystins act as global modifiers of cilium structure
Abstract
Nephronophthisis (NPHP) is the most common genetic cause of end-stage renal disease in children and young adults. In Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Caenorhabditis elegans, and mammals, the NPHP1 and NPHP4 gene products nephrocystin-1 and nephrocystin-4 localize to basal bodies or ciliary transition zones (TZs), but their function in this location remains unknown. We show here that loss of C. elegans NPHP-1 and NPHP-4 from TZs is tolerated in developing cilia but causes changes in localization of specific ciliary components and a broad range of subtle axonemal ultrastructural defects. In amphid channel cilia, nphp-4 mutations cause B tubule defects that further disrupt intraflagellar transport (IFT). We propose that NPHP-1 and NPHP-4 act globally at the TZ to regulate ciliary access of the IFT machinery, axonemal structural components, and signaling molecules, and that perturbing this balance results in cell type-specific phenotypes.
Figures
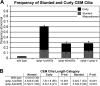
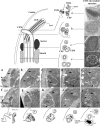
Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of the C. elegans nephrocystins NPHP-1 and NPHP-4 and their role in cilia and male sensory behaviors.Exp Cell Res. 2005 May 1;305(2):333-42. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.01.008. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15817158
-
A Screen for Modifiers of Cilia Phenotypes Reveals Novel MKS Alleles and Uncovers a Specific Genetic Interaction between osm-3 and nphp-4.PLoS Genet. 2016 Feb 10;12(2):e1005841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005841. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26863025 Free PMC article.
-
The nphp-2 and arl-13 genetic modules interact to regulate ciliogenesis and ciliary microtubule patterning in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2014 Dec 11;10(12):e1004866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004866. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25501555 Free PMC article.
-
The ciliary transitional zone and nephrocystins.Differentiation. 2012 Feb;83(2):S91-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2011.11.006. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Differentiation. 2012. PMID: 22169048 Review.
-
Nephronophthisis.Pediatr Nephrol. 2011 Feb;26(2):181-94. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1585-z. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 20652329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish dscaml1 Deficiency Impairs Retinal Patterning and Oculomotor Function.J Neurosci. 2020 Jan 2;40(1):143-158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1783-19.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 4. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31685652 Free PMC article.
-
What drives cell morphogenesis: a look inside the vertebrate photoreceptor.Dev Dyn. 2009 Sep;238(9):2115-38. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22010. Dev Dyn. 2009. PMID: 19582864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraflagellar transport at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 1;122(Pt 7):889-92. doi: 10.1242/jcs.023861. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19295122 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MKS5 and CEP290 Dependent Assembly Pathway of the Ciliary Transition Zone.PLoS Biol. 2016 Mar 16;14(3):e1002416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002416. eCollection 2016 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 26982032 Free PMC article.
-
Partially Redundant Actin Genes in Chlamydomonas Control Transition Zone Organization and Flagellum-Directed Traffic.Cell Rep. 2019 May 21;27(8):2459-2467.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.087. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31116988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arts, H.H., D. Doherty, S.E. van Beersum, M.A. Parisi, S.J. Letteboer, N.T. Gorden, T.A. Peters, T. Marker, K. Voesenek, A. Kartono, et al. 2007. Mutations in the gene encoding the basal body protein RPGRIP1L, a nephrocystin-4 interactor, cause Joubert syndrome. Nat. Genet. 39:882–888. - PubMed
-
- Attanasio, M., N.H. Uhlenhaut, V.H. Sousa, J.F. O'Toole, E. Otto, K. Anlag, C. Klugmann, A.C. Treier, J. Helou, J.A. Sayer, et al. 2007. Loss of GLIS2 causes nephronophthisis in humans and mice by increased apoptosis and fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 39:1018–1024. - PubMed
-
- Badano, J.L., N. Mitsuma, P.L. Beales, and N. Katsanis. 2006. The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 7:125–148. - PubMed
-
- Bae, Y.K., H. Qin, K.M. Knobel, J. Hu, J.L. Rosenbaum, and M.M. Barr. 2006. General and cell-type specific mechanisms target TRPP2/PKD-2 to cilia. Development. 133:3859–3870. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann, C.I. 2006. Related comparative chemosensation from receptors to ecology. Nature. 444:295–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

