Functional interaction between Wnt3 and Frizzled-7 leads to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 18313787
- PMCID: PMC2390890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.12.020
Functional interaction between Wnt3 and Frizzled-7 leads to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background/aims: The canonical Wnt signaling is frequently activated in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We previously demonstrated that upregulation of Frizzled-7 receptor (FZD7) in HCC was associated with nuclear accumulation of wild-type beta-catenin. Here, we investigated Wnt ligand(s) that may activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway through FZD7 in HCC cells.
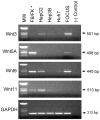
Methods: To identify Wnt ligand expression, RT-PCR was performed in HCC cells. To evaluate the function of Wnt3 and FZD7 in HCC, we utilized Wnt3 overexpressing FOCUS HCC cells (FOCUS-Wnt3) and human tumors.
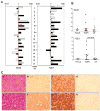
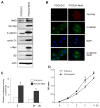
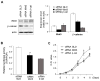
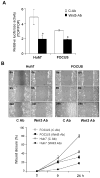
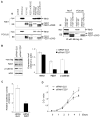
Results: In hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced HCC, Wnt3 was upregulated in tumor and peritumoral tissues compared to normal liver and downstream beta-catenin target genes were also increased in these samples. Activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in FOCUS-Wnt3 cells was demonstrated by beta-catenin accumulation, enhanced TCF transcriptional activity and proliferation rate. The activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in FOCUS-Wnt3 was abolished by a knockdown of FZD7 expression by siRNA. More important, a specific Wnt3-FZD7 interaction was observed by co-immunoprecipitation experiments, which suggest that the action of Wnt3 was mediated via FZD7.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate a functional interaction between Wnt3 and FZD7 leading to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in HCC cells and may play a role during hepatocarcinogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble Frizzled-7 receptor inhibits Wnt signaling and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards doxorubicin.Mol Cancer. 2011 Feb 11;10:16. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-16. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21314951 Free PMC article.
-
Functional consequences of frizzled-7 receptor overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2004 Oct;127(4):1110-22. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.07.009. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15480989
-
Oncogenic role of the frizzled-7/beta-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2005 Nov;43(5):854-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.05.018. Epub 2005 Jun 21. J Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 16098625
-
Frizzled7 as an emerging target for cancer therapy.Cell Signal. 2012 Apr;24(4):846-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.12.009. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22182510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of Wnt β-catenin pathway and miRNAs in HBV pathogenesis leading to HCC.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;43(4):373-386. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30377095 Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in liver biology and tumorigenesis.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 May;60(5):466-481. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00858-7. Epub 2024 Feb 20. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38379098 Review.
-
Molecular signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma: Role of and crosstalk among WNT/ß-catenin, Sonic Hedgehog, Notch and Dickkopf-1.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 May;29(4):209-17. doi: 10.1155/2015/172356. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25965442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-2053 overexpression inhibits the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):2043-2049. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10501. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423276 Free PMC article.
-
Gene signatures derived from a c-MET-driven liver cancer mouse model predict survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024582. Epub 2011 Sep 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21949730 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt-/-β-catenin pathway signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Hepatol. 2015 Nov 18;7(26):2631-5. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i26.2631. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26609340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810. - PubMed
-
- Caricasole AFT, Iacovelli L, Barletta E, Caruso A, Melchiorri D, Terstappen GC, et al. Functional characterization of Wnt7a signaling in PC12 cells: interaction with A FZD5 x LRP6 receptor complex and modulation by Dickkopf proteins. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:37024. - PubMed
-
- Winn RA, Marek L, Han SY, Rodriguez K, Rodriguez N, Hammond M, et al. Restoration of Wnt-7a expression reverses non-small cell lung cancer cellular transformation through frizzled-9-mediated growth inhibition and promotion of cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:19625–19634. - PubMed
-
- Gazit A, Yaniv A, Bafico A, Pramila T, Igarashi M, Kitajewski J, et al. Human frizzled 1 interacts with transforming Wnts transduce a TCF dependent transcriptional response. Oncogene. 1999;18:5959–5966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

