Comprehensive analysis of PPARalpha-dependent regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by expression profiling
- PMID: 18288265
- PMCID: PMC2233741
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/26839
Comprehensive analysis of PPARalpha-dependent regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by expression profiling
Abstract
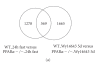
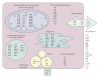
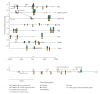
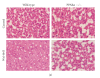
PPARalpha is a ligand-activated transcription factor involved in the regulation of nutrient metabolism and inflammation. Although much is already known about the function of PPARalpha in hepatic lipid metabolism, many PPARalpha-dependent pathways and genes have yet to be discovered. In order to obtain an overview of PPARalpha-regulated genes relevant to lipid metabolism, and to probe for novel candidate PPARalpha target genes, livers from several animal studies in which PPARalpha was activated and/or disabled were analyzed by Affymetrix GeneChips. Numerous novel PPARalpha-regulated genes relevant to lipid metabolism were identified. Out of this set of genes, eight genes were singled out for study of PPARalpha-dependent regulation in mouse liver and in mouse, rat, and human primary hepatocytes, including thioredoxin interacting protein (Txnip), electron-transferring-flavoprotein beta polypeptide (Etfb), electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase (Etfdh), phosphatidylcholine transfer protein (Pctp), endothelial lipase (EL, Lipg), adipose triglyceride lipase (Pnpla2), hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL, Lipe), and monoglyceride lipase (Mgll). Using an in silico screening approach, one or more PPAR response elements (PPREs) were identified in each of these genes. Regulation of Pnpla2, Lipe, and Mgll, which are involved in triglyceride hydrolysis, was studied under conditions of elevated hepatic lipids. In wild-type mice fed a high fat diet, the decrease in hepatic lipids following treatment with the PPARalpha agonist Wy14643 was paralleled by significant up-regulation of Pnpla2, Lipe, and Mgll, suggesting that induction of triglyceride hydrolysis may contribute to the anti-steatotic role of PPARalpha. Our study illustrates the power of transcriptional profiling to uncover novel PPARalpha-regulated genes and pathways in liver.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of gene regulation by the transcription factor PPARalpha between mouse and human.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 27;4(8):e6796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006796. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19710929 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic signatures of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in different mouse liver models identify novel aspects of its biology.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 15;15(1):1106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1106. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25511156 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of PPARα activation on whole genome gene expression in human precision cut liver slices.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 8;16:760. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1969-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26449539 Free PMC article.
-
The role and regulation of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha in human liver.Biochimie. 2017 May;136:75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.019. Epub 2017 Jan 8. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28077274 Review.
-
Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:124-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24362249 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-hyperlipidemic effects and potential mechanisms of action of the caffeoylquinic acid-rich Pandanus tectorius fruit extract in hamsters fed a high fat-diet.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 16;8(4):e61922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061922. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613974 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids in liver disease: looking beyond steatosis.Gastroenterology. 2012 Jan;142(1):8-11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22107717 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Statistical Approach to Compare Transcriptomics Data Across Experiments: A Case Study on the Identification of Candidate Target Genes of the Transcription Factor PPARα.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2012;6:145-54. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S9529. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2012. PMID: 22783064 Free PMC article.
-
Histone methyltransferase Smyd1 regulates mitochondrial energetics in the heart.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Aug 14;115(33):E7871-E7880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1800680115. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30061404 Free PMC article.
-
Lipolysis: cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores.Nat Metab. 2021 Nov;3(11):1445-1465. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00493-6. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Nat Metab. 2021. PMID: 34799702 Review.
References
-
- Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 2000;405(6785):421–424. - PubMed
-
- Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang Y-X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nature Medicine. 2004;10(4):355–361. - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocrine Reviews. 1999;20(5):649–688. - PubMed
-
- Bocher V, Pineda-Torra I, Fruchart J-C, Staels B. PPARs: transcription factors controlling lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2002;967:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Smith SA. Peroxisomal proliferater-activated receptors and the regulation of lipid oxidation and adipogenesis. Biochemical Society Transactions. 1997;25(4):1242–1248. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

