MicroRNA Mirn140 modulates Pdgf signaling during palatogenesis
- PMID: 18264099
- PMCID: PMC2747601
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.82
MicroRNA Mirn140 modulates Pdgf signaling during palatogenesis
Abstract
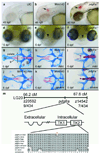
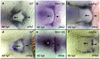
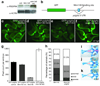
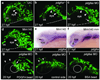
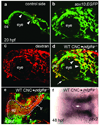
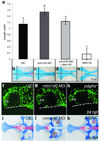
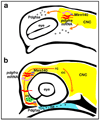
Disruption of signaling pathways such as those mediated by sonic hedgehog (Shh) or platelet-derived growth factor (Pdgf) causes craniofacial abnormalities, including cleft palate. The role that microRNAs play in modulating palatogenesis, however, is completely unknown. We show that, in zebrafish, the microRNA Mirn140 negatively regulates Pdgf signaling during palatal development, and we provide a mechanism for how disruption of Pdgf signaling causes palatal clefting. The pdgf receptor alpha (pdgfra) 3' UTR contained a Mirn140 binding site functioning in the negative regulation of Pdgfra protein levels in vivo. pdgfra mutants and Mirn140-injected embryos shared a range of facial defects, including clefting of the crest-derived cartilages that develop in the roof of the larval mouth. Concomitantly, the oral ectoderm beneath where these cartilages develop lost pitx2 and shha expression. Mirn140 modulated Pdgf-mediated attraction of cranial neural crest cells to the oral ectoderm, where crest-derived signals were necessary for oral ectodermal gene expression. Mirn140 loss of function elevated Pdgfra protein levels, altered palatal shape and caused neural crest cells to accumulate around the optic stalk, a source of the ligand Pdgfaa. These results suggest that the conserved regulatory interactions of mirn140 and pdgfra define an ancient mechanism of palatogenesis, and they provide candidate genes for cleft palate.
Figures

Comment in
-
MicroRNAs in facial development.Nat Genet. 2008 Mar;40(3):268-9. doi: 10.1038/ng0308-268. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18305475 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Pdgfra and Pdgfrb genetically interact during craniofacial development.Dev Dyn. 2016 Jun;245(6):641-52. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24403. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Dev Dyn. 2016. PMID: 26971580 Free PMC article.
-
Pdgfra protects against ethanol-induced craniofacial defects in a zebrafish model of FASD.Development. 2013 Aug;140(15):3254-65. doi: 10.1242/dev.094938. Development. 2013. PMID: 23861062 Free PMC article.
-
A specific requirement for PDGF-C in palate formation and PDGFR-alpha signaling.Nat Genet. 2004 Oct;36(10):1111-6. doi: 10.1038/ng1415. Epub 2004 Sep 7. Nat Genet. 2004. PMID: 15361870
-
PDGF function in diverse neural crest cell populations.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Oct-Dec;4(4):561-6. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.4.12829. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20657170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Facial Morphogenesis: Physical and Molecular Interactions Between the Brain and the Face.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;115:299-320. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26589930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-environment interactions in development and disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2017 Jan;6(1):10.1002/wdev.247. doi: 10.1002/wdev.247. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27626243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cranial neural crest migration: new rules for an old road.Dev Biol. 2010 Aug 15;344(2):543-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.04.010. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20399765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The midline, oral ectoderm, and the arch-0 problem.Integr Comp Biol. 2008 Nov;48(5):668-80. doi: 10.1093/icb/icn048. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Integr Comp Biol. 2008. PMID: 20585416 Free PMC article.
-
Unique organization of the frontonasal ectodermal zone in birds and mammals.Dev Biol. 2009 Jan 1;325(1):200-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.026. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19013147 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish models of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Genesis. 2021 Nov;59(11):e23460. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23460. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Genesis. 2021. PMID: 34739740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Osumi-Yamashita N, Ninomiya Y, Doi H, Eto K. The contribution of both forebrain and midbrain crest cells to the mesenchyme in the frontonasal mass of mouse embryos. Developmental Biology. 1994;164:409–419. - PubMed
-
- Trainor PA, Melton KR, Manzanares M. Origins and plasticity of neural crest cells and their roles in jaw and craniofacial evolution. International Journal of Developmental Biology. 2003;47:541–553. - PubMed
-
- Wada N, et al. Hedgehog signaling is required for cranial neural crest morphogenesis and chondrogenesis at the midline in the zebrafish skull. Development. 2005;132:3977–3988. - PubMed
-
- Eberhart JK, Swartz ME, Crump JG, Kimmel CB. Early Hedgehog signaling from neural to oral epithelium organizes anterior craniofacial development. Development. 2006;133:1069–1077. - PubMed
-
- Trainor PA, Krumlauf R. Hox genes, neural crest cells and branchial arch patterning. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2001;13:698–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R00 DE018088-03/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 5 K99 DE018088/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 RR020833/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DE018088-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DE018088/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD22486/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 RR020833-03/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01RR020833/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DE018088/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DE018088-02/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD022486/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD022486-220001/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD022486-159007/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 RR020833-04/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD022486-169007/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD022486-22/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

