Progenitor/stem cells give rise to liver cancer due to aberrant TGF-beta and IL-6 signaling
- PMID: 18263735
- PMCID: PMC2268156
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705395105
Progenitor/stem cells give rise to liver cancer due to aberrant TGF-beta and IL-6 signaling
Abstract
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are critical for the initiation, propagation, and treatment resistance of multiple cancers. Yet functional interactions between specific signaling pathways in solid organ "cancer stem cells," such as those of the liver, remain elusive. We report that in regenerating human liver, two to four cells per 30,000-50,000 cells express stem cell proteins Stat3, Oct4, and Nanog, along with the prodifferentiation proteins TGF-beta-receptor type II (TBRII) and embryonic liver fodrin (ELF). Examination of human hepatocellular cancer (HCC) reveals cells that label with stem cell markers that have unexpectedly lost TBRII and ELF. elf(+/-) mice spontaneously develop HCC; expression analysis of these tumors highlighted the marked activation of the genes involved in the IL-6 signaling pathway, including IL-6 and Stat3, suggesting that HCC could arise from an IL-6-driven transformed stem cell with inactivated TGF-beta signaling. Similarly, suppression of IL-6 signaling, through the generation of mouse knockouts involving a positive regulator of IL-6, Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor-heavy chain-4 (ITIH4), resulted in reduction in HCC in elf(+/-) mice. This study reveals an unexpected functional link between IL-6, a major stem cell signaling pathway, and the TGF-beta signaling pathway in the modulation of mammalian HCC, a lethal cancer of the foregut. These experiments suggest an important therapeutic role for targeting IL-6 in HCCs lacking a functional TGF-beta pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
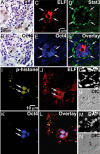
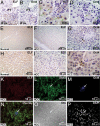
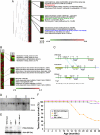
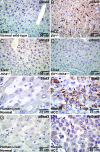
Comment in
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma development requires hepatic stem cells with altered transforming growth factor and interleukin-6 signaling.Hepatology. 2008 Jun;47(6):2134-6. doi: 10.1002/hep.22369. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18508299 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Hepatocellular cancer arises from loss of transforming growth factor beta signaling adaptor protein embryonic liver fodrin through abnormal angiogenesis.Hepatology. 2008 Oct;48(4):1128-37. doi: 10.1002/hep.22460. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18704924 Free PMC article.
-
The STAT3 inhibitor NSC 74859 is effective in hepatocellular cancers with disrupted TGF-beta signaling.Oncogene. 2009 Feb 19;28(7):961-72. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.448. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19137011 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Oct4 in HCC and modulation to wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β signal pathways.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Oct;343(1-2):155-62. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0509-3. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20549546
-
Cancer stem cells and hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Sep;8(18):1691-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.18.9843. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19901516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PRAJA and ELF in TGF-beta signaling and gastric cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jul;4(7):694-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.7.2015. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16096365 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer stem cells in the development of liver cancer.J Clin Invest. 2013 May;123(5):1911-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI66024. Epub 2013 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23635789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Contributes to Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Targeting Cancer Stem Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 30;13:9721-9730. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S262089. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Aug 22;15:871-872. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S386447 PMID: 33061451 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Quantitative impedimetric monitoring of cell migration under the stimulation of cytokine or anti-cancer drug in a microfluidic chip.Biomicrofluidics. 2015 Jun 12;9(3):034109. doi: 10.1063/1.4922488. eCollection 2015 May. Biomicrofluidics. 2015. PMID: 26180566 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β1 as a Predictor for the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nested Case-Controlled Study.EBioMedicine. 2016 Oct;12:68-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 2. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27614396 Free PMC article.
-
Growth factor- and cytokine-driven pathways governing liver stemness and differentiation.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov 7;16(41):5148-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i41.5148. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21049549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergsagel DE, Valeriote FA. Cancer Res. 1968;28:2187–2196. - PubMed
-
- Salsbury AJ. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975;2:55–72. - PubMed
-
- Morrison SJ, Kimble J. Nature. 2006;441:1068–1074. - PubMed
-
- Mishra L, Derynck R, Mishra B. Science. 2005;310:68–71. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

