Estrogen Receptors alpha and beta as determinants of gene expression: influence of ligand, dose, and chromatin binding
- PMID: 18258689
- PMCID: PMC2366177
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0356
Estrogen Receptors alpha and beta as determinants of gene expression: influence of ligand, dose, and chromatin binding
Abstract
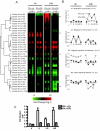
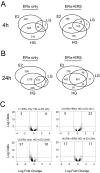
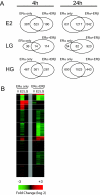
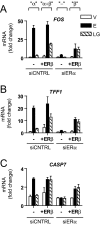
Estrogen receptors alpha and beta (ERalpha and ERbeta) mediate the actions of estrogens in a variety of normal and cancer target cells. Estrogens differ in their preference for these ERs, and many phytoestrogens bind preferentially to ERbeta. To investigate how phytoestrogens such as genistein impact ER-regulated gene expression, we used adenoviral gene delivery of ERbeta coupled with ERalpha depletion with small interfering RNA to generate human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells expressing four complements of ERalpha and ERbeta. We examined the dose-dependent effects of genistein on genome-wide gene expression by DNA microarrays and monitored the recruitment of ERs and coregulators to responsive regions of estrogen-regulated genes. At a low (6 nm) concentration, genistein regulated gene expression much more effectively in cells coexpressing ERalpha and ERbeta than in cells expressing ERalpha alone, whereas at high concentration (300 nm), genistein induced transcriptome changes very similar to that of 17beta-estradiol. We demonstrate that ERbeta is preferentially activated by genistein and is recruited to estrogen-responsive genomic sites and that differential occupancy of ERalpha and ERbeta by genistein and 17beta-estradiol in turn influences the recruitment patterns of coregulators such as steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC3) and receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140). Our observations indicate that genistein is a potency-selective ligand for gene expression regulation by ERalpha and ERbeta and that the ability of ERalpha and ERbeta to serve as determinants of gene expression is greatly influenced by the nature of the ligand, by ligand dose, and by the differential abilities of ligand-ER complexes to recruit different coregulators at ER binding sites of hormone-regulated genes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oestrogen receptors pathways to oestrogen responsive elements: the transactivation function-1 acts as the keystone of oestrogen receptor (ER)beta-mediated transcriptional repression of ERalpha.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 May;104(3-5):110-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.03.002. Epub 2007 Mar 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17478088
-
Impact of estrogen receptor beta on gene networks regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells.Endocrinology. 2006 Oct;147(10):4831-42. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0563. Epub 2006 Jun 29. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16809442
-
Cell proliferation and modulation of interaction of estrogen receptors with coregulators induced by ERα and ERβ agonists.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;143:376-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24923734
-
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 30;74(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00104-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11162936 Review.
-
Estrogen signaling via estrogen receptor {beta}.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 17;285(51):39575-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R110.180109. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20956532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genistein and bisphenol A exposure cause estrogen receptor 1 to bind thousands of sites in a cell type-specific manner.Genome Res. 2012 Nov;22(11):2153-62. doi: 10.1101/gr.135681.111. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 23019147 Free PMC article.
-
Is soy consumption good or bad for the breast?J Nutr. 2010 Dec;140(12):2326S-2334S. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.124230. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20980638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genistein stimulates jejunum chloride secretion via an Akt-mediated pathway in intact female mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(4):1317-25. doi: 10.1159/000373953. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25721972 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor β (ERβ1) transactivation is differentially modulated by the transcriptional coregulator Tip60 in a cis-acting element-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25038-25052. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476952. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23857583 Free PMC article.
-
Thiophene-core estrogen receptor ligands having superagonist activity.J Med Chem. 2013 Apr 25;56(8):3346-66. doi: 10.1021/jm400157e. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23586645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris HA 2007 Estrogen receptor-β: recent lessons from in vivo studies. Mol Endocrinol 21:1–13 - PubMed
-
- Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, Enmark E, Pettersson K, Warner M, Gustafsson JA 2001 Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev 81:1535–1565 - PubMed
-
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA 1997 Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors α and β. Endocrinology 138:863–870 - PubMed
-
- Hall JM, McDonnell DP 1999 The estrogen receptor β-isoform (ERβ) of the human estrogen receptor modulates ERα transcriptional activity and is a key regulator of the cellular response to estrogens and antiestrogens. Endocrinology 140:5566–5578 - PubMed
-
- Katzenellenbogen BS, Frasor J 2004 Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway. Semin Oncol 31:28–38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

