TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells requires pp60(c-src)/EGFR(Y845) and Rho/ROCK signaling
- PMID: 18255094
- PMCID: PMC2394714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.12.006
TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells requires pp60(c-src)/EGFR(Y845) and Rho/ROCK signaling
Abstract
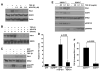
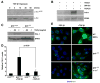
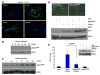
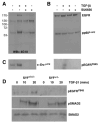
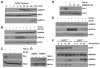
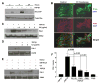
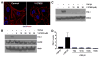
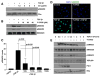
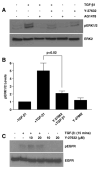
TGF-beta1 and its target gene encoding plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) are major causative factors in the pathology of tissue fibrosis and vascular disease. The increasing complexity of TGF-beta1 action in the cardiovascular system requires analysis of specific TGF-beta1-initiated signaling events that impact PAI-1 transcriptional regulation in a physiologically-relevant cell system. TGF-beta1-induced PAI-1 expression in both primary cultures and in an established line (R22) of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) was completely blocked by inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activity or adenoviral delivery of a kinase-dead EGFR(K721A) construct. TGF-beta1-stimulated PAI-1 expression, moreover, was preceded by EGFR phosphorylation on Y845 (a src kinase target residue) and required pp60(c-src) activity. Infection of VSMC with an adenovirus encoding the EGFR(Y845F) mutant or transfection with a dominant-negative pp60(c-src) (DN-Src) expression vector effectively decreased TGF-beta1-stimulated, but not PDGF-induced, PAI-1 expression implicating the pp60(c-src) phosphorylation site EGFR(Y845) in the inductive response. Consistent with these findings, TGF-beta1 failed to induce PAI-1 synthesis in src kinase-deficient (SYF(-/-/-)) fibroblasts and reexpression of a wild-type pp60(c-src) construct in SYF(-/-/-) cells rescued the PAI-1 response to TGF-beta1. TGF-beta1-induced EGFR activation, but not SMAD2 activation, moreover, was virtually undetectable in SYK(-/-/-) fibroblasts in comparison to wild type (SYK(+/+/+)) counterparts, confirming an upstream signaling role of src family kinases in EGFR(Y845) phosphorylation. Genetic EGFR deficiency or infection of VSMCs with EGFR(K721A) virtually ablated TGF-beta1-stimulated ERK1/2 activation as well as PAI-1 expression but not SMAD2 phosphorylation. Transient transfection of a dominant-negative RhoA (DN-RhoA) expression construct or pretreatment of VSMC with C3 transferase (a Rho inhibitor) or Y-27632 (an inhibitor of p160ROCK, a downstream effector of Rho) also dramatically attenuated the TGF-beta1-initiated PAI-1 inductive response. In contrast to EGFR pathway blockade, interference with Rho/ROCK signaling effectively inhibited TGF-betaR-mediated SMAD2 phosphorylation and nuclear accumulation. TGF-beta1-stimulated SMAD2 activation, moreover, was not sufficient to induce PAI-1 expression in the absence of EGFR signaling both in VSMC and mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Thus, two distinct pathways involving the EGFR/pp60(c-src)/MEK-ERK pathway and Rho/ROCK-dependent SMAD2 activation are required for TGF-beta1-induced PAI-1 expression in VSMC. The identification of such novel interactions between two TGF-beta1-activated signaling networks that specifically impact PAI-1 transcription in VSMC may provide therapeutically-relevant targets to manage the pathophysiology of PAI-1-associated cardiovascular/fibrotic diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Redox-induced Src kinase and caveolin-1 signaling in TGF-β1-initiated SMAD2/3 activation and PAI-1 expression.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022896. Epub 2011 Jul 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829547 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression and induced migration in TGF-beta1-stimulated smooth muscle cells is pp60(c-src)/MEK-dependent.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Jul;204(1):236-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20279. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15622520
-
Integration of non-SMAD and SMAD signaling in TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):976-83. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential requirement for MEK/ERK and SMAD signaling in PAI-1 and CTGF expression in response to microtubule disruption.Cell Signal. 2009 Jun;21(6):986-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.02.007. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19249354 Free PMC article.
-
The TGF-β1/p53/PAI-1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Senescence: Role of Caveolin-1.Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 3;9(8):341. doi: 10.3390/biom9080341. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31382626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelin-1 Stimulates PAI-1 Protein Expression via Dual Transactivation Pathway Dependent ROCK and Phosphorylation of Smad2L.Cell J. 2022 Aug 28;24(8):465-472. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7720. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 36093806 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of niclosamide on the intra-abdominal inflammatory environment in endometriosis.FASEB J. 2021 May;35(5):e21584. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002541RRR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33860549 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated systemic TGF-beta impairs aortic vasomotor function through activation of NADPH oxidase-driven superoxide production and leads to hypertension, myocardial remodeling, and increased plaque formation in apoE(-/-) mice.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Aug;299(2):H386-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01042.2009. Epub 2010 May 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20511416 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) treatment enhances wound closure and tissue regeneration.NPJ Regen Med. 2022 Jun 24;7(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41536-022-00228-5. NPJ Regen Med. 2022. PMID: 35750773 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 18;24(18):14229. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814229. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kutz SM, Hordines J, McKeown-Longo PJ, Higgins PJ. TGF-β1-induced PAI-1 gene expression requires MEK activity and cell-to-substrate adhesion. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:3905–14. - PubMed
-
- Yue J, Mulder KM. Transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction in epithelial cells. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;91:1–34. - PubMed
-
- Bottinger EP, Bitzer M. TGF-β signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2600–10. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang Y. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature. 2003;425:577–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

