Antiviral and anticancer optimization studies of the DNA-binding marine natural product aaptamine
- PMID: 18251774
- PMCID: PMC4918911
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00628.x
Antiviral and anticancer optimization studies of the DNA-binding marine natural product aaptamine
Abstract
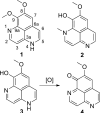
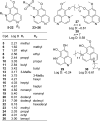
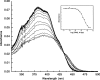
Aaptamine has potent cytotoxicity that may be explained by its ability to intercalate DNA. Aaptamine was evaluated for its ability to bind to DNA to validate DNA binding as the primary mechanism of cytotoxicity. Based on UV-vis absorbance titration data, the K(obs) for aaptamine was 4.0 (+/-0.2) x 10(3) which was essentially equivalent to the known DNA intercalator N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-9-aminoacridine-4-carboxamide. Semi-synthetic core modifications were performed to improve the general structural diversity of known aaptamine analogs and vary its absorption characteristics. Overall, 26 aaptamine derivatives were synthesized which consisted of a simple homologous range of mono and di-N-alkylations as well as some 9-O-sulfonylation and bis-O-isoaaptamine dimer products. Each product was evaluated for activity in a variety of whole cell and viral assays including a unique solid tumor disk diffusion assay. Details of aaptamine's DNA-binding activity and its derivatives' whole cell and viral assay results are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review on marine sponge alkaloid, aaptamine: A potential antibacterial and anticancer drug.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Jan;99(1):103-110. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13932. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34331335 Review.
-
Antineoplastic agents 491. Synthetic conversion of aaptamine to isoaaptamine, 9-demethylaaptamine, and 4-methylaaptamine.J Org Chem. 2004 Apr 2;69(7):2251-6. doi: 10.1021/jo0300486. J Org Chem. 2004. PMID: 15049616
-
Structures and cytotoxicity relationship of isoaaptamine and aaptamine derivatives.J Nat Prod. 1999 Sep;62(9):1264-7. doi: 10.1021/np990156g. J Nat Prod. 1999. PMID: 10514310
-
Zebra mussel antifouling activity of the marine natural product aaptamine and analogs.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2006 Jul-Aug;8(4):366-72. doi: 10.1007/s10126-005-6055-4. Epub 2006 May 26. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2006. PMID: 16718618 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-Derived Natural Lead Compound Disulfide-Linked Dimer Psammaplin A: Biological Activity and Structural Modification.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jun 27;17(7):384. doi: 10.3390/md17070384. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31252563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An efficient and cost-effective approach to kahalalide F N-terminal modifications using a nuisance algal bloom of Bryopsis pennata.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1850(9):1849-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25964068 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Optimization of 1H-1,2,3-Triazole-4-carboxamides as Novel, Potent, and Selective Inverse Agonists and Antagonists of PXR.J Med Chem. 2022 Dec 22;65(24):16829-16859. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01640. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36480704 Free PMC article.
-
Aaptamine attenuates the proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):1044-1054. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1822420. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 33027592 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in exploring the therapeutic potential of marine natural products.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Sep;147:104373. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104373. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31351913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Activity of Naturally Derived Naphthyridines.Molecules. 2021 Jul 16;26(14):4324. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144324. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakamura H, Kobayashi J, Ohizumi Y, Hirata Y. Isolation and structure of aaptamine, a novel heteroaromatic substance possessing α-blocking activity from the sea sponge Aaptos aaptos. Tetrahedron Letters. 1982;23:5555–5558.
-
- Nakamura H, Kobayashi J, Ohizumi Y, Hirata Y. Physiologically active marine natural products from Prolifera. Part 10. Aaptamines. Novel benzo[de][1,6]naphthyridines from the Okinawan marine sponge Aaptos aaptos. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1987;1:173–176.
-
- Park SK, Kim SS, Park JD, Hong JS, Kim IK. A study on the chemical constituents from marine sponge Luffariella sp. J Korean Chem Soc. 1995;39:559–563.
-
- Shen Y-C, Chein C-C, Hsieh P-W, Duh C-Y. Bioactive constituents from marine sponge Aaptos aaptos. Taiwan Shuichan Xuehuikan. 1997;24:117–125.
-
- Coutinho A, Chanas B, Souza T, Frugrulhetti I, Epifanio R. Anti HSV-1 alkaloids from a feeding deterrent marine sponge of the genus Aaptos. Heterocylces. 2002;57:1265–1272.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

