HIV-1 Tat inhibits NGF-induced Egr-1 transcriptional activity and consequent p35 expression in neural cells
- PMID: 18247371
- PMCID: PMC2712724
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21382
HIV-1 Tat inhibits NGF-induced Egr-1 transcriptional activity and consequent p35 expression in neural cells
Abstract
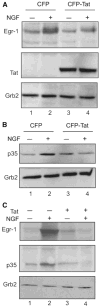
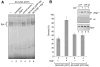
Infection with HIV-1 causes degeneration of neurons leading to motor and cognitive dysfunction in AIDS patients. One of the key viral regulatory proteins, Tat, which is released by infected cells, can be taken up by various uninfected cells including neurons and by dysregulating several biological events induces cell injury and death. In earlier studies, we demonstrated that treatment of neuronal cells with Tat affects the nerve growth factor (NGF) signaling pathway involving MAPK/ERK. Here we demonstrate that a decrease in the level of Egr-1, one of the targets for MAPK, by Tat has a negative impact on the level of p35 expression in NGF-treated neural cells. Further, we demonstrate a reduced level of Egr-1 association with the p35 promoter sequence in NGF-treated cells expressing Tat. As p35, by associating with Cdk5, phosphorylates several neuronal proteins including neurofilaments and plays a role in neuronal differentiation and survival, we examined kinase activity of p35 complexes obtained from cells expressing Tat. Results from H1 kinase assays showed reduced activity of the p35 complex from Tat-expressing cells in comparison to that from control cells. Accordingly, the level of phosphorylated neurofilaments was diminished in Tat-expressing cells. Similarly, treatment of PC12 cells with Tat protein or supernatant from HIV-1 infected cells decreased kinase activity of p35 in these cells. These observations ascribe a role for Tat in altering p35 expression and its activity that affects phosphorylation of proteins involved in neuronal cell survival.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
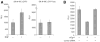
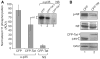
Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of NGF-signaling and Egr-1 expression by Tat in neuronal cell culture.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Sep;208(3):506-15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20675. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16741963
-
Tat-induced deregulation of neuronal differentiation and survival by nerve growth factor pathway.J Neurovirol. 2002 Dec;8 Suppl 2:91-6. doi: 10.1080/13550280290167885. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12491158 Review.
-
Metformin inhibits nerve growth factor-induced sympathetic neuron differentiation through p35/CDK5 inhibition.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Jun 1;326(6):C1648-C1658. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00121.2024. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38682237
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulates cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity during pain signaling through transcriptional activation of p35.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 23;284(4):2275-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805052200. Epub 2008 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19049962 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat neurotoxicity via CDK5 translocation and hyper-activation: role in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.Curr HIV Res. 2015;13(1):43-54. doi: 10.2174/1570162x13666150311164201. Curr HIV Res. 2015. PMID: 25760044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of neurotrophic factor alterations in the neurodegenerative process in HIV associated neurocognitive disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;9(2):102-16. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9520-2. Epub 2014 Feb 8. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24510686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inhibition of microRNAs by HIV-1 Tat suppresses beta catenin activity in astrocytes.Retrovirology. 2016 Apr 8;13:25. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0256-y. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 27060080 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicity of human immunodeficiency virus-1: viral proteins and axonal transport.Neurotox Res. 2012 Jan;21(1):79-89. doi: 10.1007/s12640-011-9279-2. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 21948112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophins modulate the expression of chemokine receptors in the brain.J Neurovirol. 2011 Feb;17(1):58-62. doi: 10.1007/s13365-010-0004-3. Epub 2010 Nov 30. J Neurovirol. 2011. PMID: 21165786 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocytoskeleton Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid of People With HIV-1 Subtypes B and C.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020 Aug 15;84(5):514-521. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002389. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32692110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adle-Biassette H, Levy Y, Colombel M, Poron F, Natchev S, Keohane C, Gray F. Neuronal apoptosis in HIV infection in adults. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1995;21:218–227. - PubMed
-
- Al-Sarraj A, Day RM, Thiel G. Specificity of transcriptional regulation by the zinc finger transcription factors Sp1, Sp3, and Egr-1. J Cell Biochem. 2005;94:153–167. - PubMed
-
- Chapman DL, Wolgemuth DJ. Regulation of M-phase promoting factor activity during development of mouse male germ cells. Dev Biol. 1994;165:500–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

