Netrin-1 is a novel myelin-associated inhibitor to axon growth
- PMID: 18234888
- PMCID: PMC6671394
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4906-07.2008
Netrin-1 is a novel myelin-associated inhibitor to axon growth
Abstract
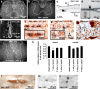
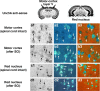
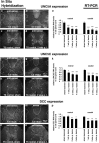
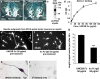
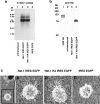
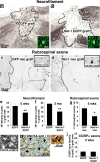
We investigated the influence of the bifunctional guidance molecule netrin-1 on axonal growth in the injured adult spinal cord. In the adult, netrin-1 is expressed on mature oligodendrocytes, cells of the central canal, and the meninges. Netrin-1 protein in white matter is selectively enriched adjacent to paranodal loops of myelin in nodes of Ranvier. The repulsion-mediating netrin-1 uncoordinated-5 (UNC5) receptors are expressed by neurons of the corticospinal and rubrospinal projections, and by intrinsic neurons of the spinal cord, both before and after spinal cord injury. Neutralization of netrin-1 in myelin prepared from adult rat spinal cord using UNC5 receptor bodies increases neurite outgrowth from UNC5-expressing spinal motor neurons in vitro. Furthermore, axon regeneration is inhibited in a netrin-1-enriched zone, devoid of other myelin-associated inhibitors, within spinal cord lesion sites in vivo. We conclude that netrin-1 is a novel oligodendrocyte-associated inhibitor that can contribute to axonal growth failure after adult spinal cord injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Widespread expression of netrin-1 by neurons and oligodendrocytes in the adult mammalian spinal cord.J Neurosci. 2001 Jun 1;21(11):3911-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-11-03911.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11356879 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Netrin-1 Signaling in Nerve Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 24;18(3):491. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030491. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28245592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positioned to inhibit: netrin-1 and netrin receptor expression after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Dec;84(8):1808-20. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21070. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16998900
-
Netrin-1 is required for the normal development of spinal cord oligodendrocytes.J Neurosci. 2006 Feb 15;26(7):1913-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3571-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16481423 Free PMC article.
-
Netrin-1 signaling for sensory axons: Involvement in sensory axonal development and regeneration.Cell Adh Migr. 2009 Apr-Jun;3(2):171-3. doi: 10.4161/cam.3.2.7837. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Cell Adh Migr. 2009. PMID: 19262170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Netrin-1 directs dendritic growth and connectivity of vertebrate central neurons in vivo.Neural Dev. 2015 Jun 10;10:14. doi: 10.1186/s13064-015-0041-y. Neural Dev. 2015. PMID: 26058786 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy approaches to enhancing plasticity and regeneration after spinal cord injury.Exp Neurol. 2012 May;235(1):62-9. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.01.015. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 21281633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of axonal regeneration after mammalian spinal cord injury.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;24(6):396-413. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00562-y. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36604586 Review.
-
The curious case of NG2 cells: transient trend or game changer?ASN Neuro. 2011 Mar 10;3(1):e00052. doi: 10.1042/AN20110001. ASN Neuro. 2011. PMID: 21288204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concepts and methods for the study of axonal regeneration in the CNS.Neuron. 2012 Jun 7;74(5):777-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.006. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22681683 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azanchi R, Bernal G, Gupta R, Keirstead HS. Combined demyelination plus Schwann cell transplantation therapy increases spread of cells and axonal regeneration following contusion injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:775–788. - PubMed
-
- Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. GDNF gene delivery to injured adult CNS motor neurons promotes axonal growth, expression of the trophic neuropeptide CGRP, and cellular protection. J Comp Neurol. 2001;436:399–410. - PubMed
-
- Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Cellular GDNF delivery promotes growth of motor and dorsal column sensory axons after partial and complete spinal cord transections and induces remyelination. J Comp Neurol. 2003;467:403–417. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB. Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2002;416:636–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
