Pioglitazone inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide synthase is associated with altered activity of p38 MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt
- PMID: 18205920
- PMCID: PMC2254610
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-4
Pioglitazone inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide synthase is associated with altered activity of p38 MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested that peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma)-mediated neuroprotection involves inhibition of microglial activation and decreased expression and activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS); however, the underlying molecular mechanisms have not yet been well established. In the present study we explored: (1) the effect of the PPAR-gamma agonist pioglitazone on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced iNOS activity and nitric oxide (NO) generation by microglia; (2) the differential role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) on LPS-induced NO generation; and (3) the regulation of p38 MAPK, JNK, and PI3K by pioglitazone.
Methods: Mesencephalic neuron-microglia mixed cultures, and microglia-enriched cultures were treated with pioglitazone and/or LPS. The protein levels of iNOS, p38 MAPK, JNK, PPAR-gamma, PI3K, and protein kinase B (Akt) were measured by western blot. Different specific inhibitors of iNOS, p38MAPK, JNK, PI3K, and Akt were used in our experiment, and NO generation was measured using a nitrite oxide assay kit. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons were counted in mesencephalic neuron-microglia mixed cultures.
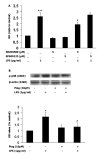
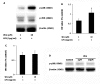
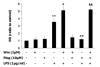
Results: Our results showed that pioglitazone inhibits LPS-induced iNOS expression and NO generation, and inhibition of iNOS is sufficient to protect dopaminergic neurons against LPS insult. In addition, inhibition of p38 MAPK, but not JNK, prevented LPS-induced NO generation. Further, and of interest, pioglitazone inhibited LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. Wortmannin, a specific PI3K inhibitor, enhanced p38 MAPK phosphorylation upon LPS stimulation of microglia. Elevations of phosphorylated PPAR-gamma, PI3K, and Akt levels were observed with pioglitazone treatment, and inhibition of PI3K activity enhanced LPS-induced NO production. Furthermore, wortmannin prevented the inhibitory effect of pioglitazone on the LPS-induced NO increase.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that pioglitazone protects dopaminergic neurons against LPS insult at least via inhibiting iNOS expression and NO generation, which is potentially mediated via inhibition of p38 MAPK activity. In addition, the PI3K pathway actively participates in the negative regulation of LPS-induced NO production. Our findings suggest that PPAR-gamma activation may involve differential regulation of p38 MAPK and of the PI3K/Akt pathway in the regulation of the inflammatory process.
Figures
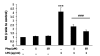
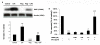
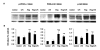
Similar articles
-
PPARγ agonist pioglitazone inhibits microglia inflammation by blocking p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Inflamm Res. 2010 Nov;59(11):921-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0203-7. Epub 2010 May 21. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20495845
-
Silymarin protects dopaminergic neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglia activation.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Dec;16(11):2103-12. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02290.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12473078
-
Thrombin-activated microglia contribute to death of dopaminergic neurons in rat mesencephalic cultures: dual roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Glia. 2005 Aug 1;51(2):98-110. doi: 10.1002/glia.20190. Glia. 2005. PMID: 15789435
-
Protective Effects of Pioglitazone on Cognitive Impairment and the Underlying Mechanisms: A Review of Literature.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Aug 31;16:2919-2931. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S367229. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36068789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating microglia activity with PPAR-γ agonists: a promising therapy for Parkinson's disease?Neurotox Res. 2013 Feb;23(2):112-23. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9342-7. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 22869006 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous GDNF Is Unable to Halt Dopaminergic Injury Triggered by Microglial Activation.Cells. 2023 Dec 29;13(1):74. doi: 10.3390/cells13010074. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201277 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y13 receptor-mediated rapid increase in intracellular calcium induced by ADP in cultured dorsal spinal cord microglia.Neurochem Res. 2014 Nov;39(11):2240-50. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1426-8. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 25186167
-
Elucidating the Neuroprotective Role of PPARs in Parkinson's Disease: A Neoteric and Prospective Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 21;22(18):10161. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810161. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silica Nanoparticle-Endothelial Interaction: Uptake and Effect on Platelet Adhesion under Flow Conditions.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018 Nov 19;1(5):1620-1627. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.8b00466. Epub 2018 Nov 30. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018. PMID: 34046558 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced innate immune response through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation in human monocytes.J Hypertens. 2012 Jan;30(1):87-96. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32834dde5f. J Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22124178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology. 1988;38:1285–1291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

