CTD kinase large subunit is encoded by CTK1, a gene required for normal growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 1820212
- PMCID: PMC5952209
CTD kinase large subunit is encoded by CTK1, a gene required for normal growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
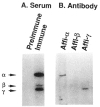
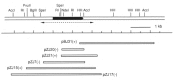
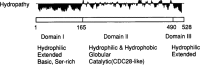
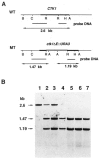
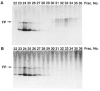
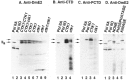
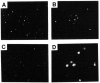
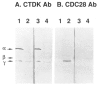
We previously purified a yeast protein kinase that specifically hyperphosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal repeat domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II largest subunit and showed that this CTD kinase consists of three subunits of 58, 38, and 32 kDa. We have now cloned, sequenced, and characterized CTK1, the gene encoding the 58 kDa alpha subunit. The CTK1 gene product contains a central domain homologous to catalytic subunits of other protein kinases, notably yeast CDC28, suggesting that the 58 kDa subunit is catalytic. Cells that carry a disrupted version of the CTK1 gene lack the characterized CTD kinase activity, grow slowly and are cold-sensitive, demonstrating that the CTK1 gene product is essential for CTD kinase activity and normal growth. While ctk1 mutant cells do contain phosphorylated forms of the RNA polymerase II largest subunit, these forms differ from those found in wild type cells, implicating CTK1 as a component of the physiologically significant CTD phosphorylating machinery. As befitting an enzyme with a nuclear function, the N-terminal region of the CTK1 protein contains a nuclear targeting signal.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CDK12 is a transcription elongation-associated CTD kinase, the metazoan ortholog of yeast Ctk1.Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 15;24(20):2303-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.1968210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20952539 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation by Cak1 regulates the C-terminal domain kinase Ctk1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 May;25(10):3906-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.10.3906-3913.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15870265 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast carboxyl-terminal repeat domain kinase CTDK-I is a divergent cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase complex.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5716-24. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.10.5716. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7565723 Free PMC article.
-
A structural perspective of CTD function.Genes Dev. 2005 Jun 15;19(12):1401-15. doi: 10.1101/gad.1318105. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15964991 Review.
-
Assaying CTD kinases in vitro and phosphorylation-modulated properties of RNA polymerase II in vivo.Methods. 1997 Jul;12(3):264-75. doi: 10.1006/meth.1997.0478. Methods. 1997. PMID: 9237170 Review.
Cited by
-
CTD kinase I is involved in RNA polymerase I transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Nov 1;32(19):5851-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh927. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15520468 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain kinases: emerging clues to their function.Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Apr;1(2):153-62. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.2.153-162.2002. Eukaryot Cell. 2002. PMID: 12455950 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain by the Bur1 cyclin-dependent kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;21(13):4089-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.13.4089-4096.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11390638 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of CTDK-I throughout the cell.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jul;76(14):2789-2797. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03118-0. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31037337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional studies of the carboxy-terminal repeat domain of Drosophila RNA polymerase II in vivo.Genetics. 1995 Jun;140(2):599-613. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.2.599. Genetics. 1995. PMID: 7498740 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
