betaKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 signaling through FGF receptor (FGFR) 1c and FGFR3c
- PMID: 18187602
- PMCID: PMC5419549
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0313
betaKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 signaling through FGF receptor (FGFR) 1c and FGFR3c
Abstract
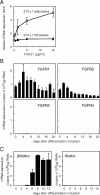
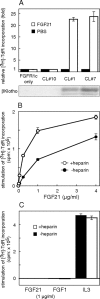
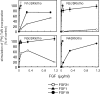
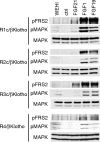
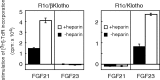
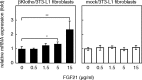
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21, a structural relative of FGF23 that regulates phosphate homeostasis, is a regulator of insulin-independent glucose transport in adipocytes and plays a role in the regulation of body weight. It also regulates ketogenesis and adaptive responses to starvation. We report that in a reconstituted receptor activation assay system using BaF3 cells, which do not endogenously express any type of FGF receptor (FGFR) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan, FGF21 alone does not activate FGFRs and that betaKlotho is required for FGF21 to activate two specific FGFR subtypes: FGFR1c and FGFR3c. Coexpression of betaKlotho and FGFR1c on BaF3 cells enabled FGF21, but not FGF23, to activate receptor signaling. Conversely, coexpression of FGFR1c and Klotho, a protein related to betaKlotho, enabled FGF23 but not FGF21 to activate receptor signaling, indicating that expression of betaKlotho/Klotho confers target cell specificity on FGF21/FGF23. In all of these cases, heparin enhanced the activation but was not essential. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, up-regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) expression by FGF21 was associated with expression of betaKlotho, which was absent in undifferentiated 3T3-L1 fibroblasts. It is thus suggested that betaKlotho expression is a crucial determinant of the FGF21 specificity of the target cells upon which it acts in an endocrine fashion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A unique FGF23 with the ability to activate FGFR signaling through both αKlotho and βKlotho.J Mol Biol. 2012 Apr 20;418(1-2):82-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.02.027. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22370560
-
Tissue-specific expression of betaKlotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 14;282(37):26687-26695. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704165200. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17623664 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile and overexpression outcome indicate a role for βKlotho in skeletal muscle fibro/adipogenesis.FEBS J. 2016 May;283(9):1653-68. doi: 10.1111/febs.13682. Epub 2016 Apr 13. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26881702 Free PMC article.
-
The Klotho proteins in health and disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019 Jan;15(1):27-44. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0078-3. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30455427 Review.
-
The Klotho gene family as a regulator of endocrine fibroblast growth factors.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009 Feb 5;299(1):72-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.10.052. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19063940 Review.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1α in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1.Springerplus. 2014 Jan 2;3:2. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-2. eCollection 2014. Springerplus. 2014. PMID: 25932355 Free PMC article.
-
Autofluorescence imaging of living pancreatic islets reveals fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21)-induced metabolism.Biophys J. 2012 Dec 5;103(11):2379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.028. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 23283237 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Control of Phosphorus Homeostasis and Precision Treatment of Hypophosphatemic Disorders.Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Jun;5(2):75-85. doi: 10.1007/s40610-019-0118-1. Epub 2019 Feb 9. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31871877 Free PMC article.
-
Mammary gland growth factors: roles in normal development and in cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Aug;2(8):a003186. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003186. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20554705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system.Nat Med. 2013 Sep;19(9):1147-52. doi: 10.1038/nm.3249. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23933984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM 2004. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet 20:563–569 - PubMed
-
- Yu X, White KE 2005. FGF23 and disorders of phosphate homeostasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:221–232 - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA 2005. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab 2:217–225 - PubMed
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N 2000. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:203–206 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

