Intermediate filaments: versatile building blocks of cell structure
- PMID: 18178072
- PMCID: PMC3243490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.11.003
Intermediate filaments: versatile building blocks of cell structure
Abstract
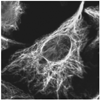
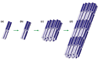
Cytoskeletal intermediate filaments (IF) are organized into a dynamic nanofibrillar complex that extends throughout mammalian cells. This organization is ideally suited to their roles as response elements in the subcellular transduction of mechanical perturbations initiated at cell surfaces. IF also provide a scaffold for other types of signal transduction that together with molecular motors ferries signaling molecules from the cell periphery to the nucleus. Recent insights into their assembly highlight the importance of co-translation of their precursors, the hierarchical organization of their subunits in the formation of unit-length filaments (ULF) and the linkage of ULF into mature apolar IF. Analyses by atomic force microscopy reveal that mature IF are flexible and can be stretched to over 300% of their length without breaking, suggesting that intrafilament subunits can slide past one another when exposed to mechanical stress and strain. IF also play a role in the organization of organelles by modulating their motility and providing anchorage sites within the cytoplasm.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The motility and dynamic properties of intermediate filaments and their constituent proteins.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jun 10;313(10):2236-43. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.04.008. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17498691 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic intermediate filaments revealed as dynamic and multipurpose scaffolds.Nat Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;6(8):699-706. doi: 10.1038/ncb0804-699. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15303099 Review.
-
Intermediate filament mechanics in vitro and in the cell: from coiled coils to filaments, fibers and networks.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;32:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25621895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly Kinetics of Vimentin Tetramers to Unit-Length Filaments: A Stopped-Flow Study.Biophys J. 2018 May 22;114(10):2408-2418. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.04.032. Epub 2018 May 10. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29754715 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical structure controls nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filaments.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 6;4(10):e7294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007294. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19806221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Subunit-dependent modulation of septin assembly: budding yeast septin Shs1 promotes ring and gauze formation.J Cell Biol. 2011 Dec 12;195(6):993-1004. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201107123. Epub 2011 Dec 5. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22144691 Free PMC article.
-
AKT1-mediated Lamin A/C degradation is required for nuclear degradation and normal epidermal terminal differentiation.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):2123-32. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.62. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 26045045 Free PMC article.
-
The desmin coil 1B mutation K190A impairs nebulin Z-disc assembly and destabilizes actin thin filaments.J Cell Sci. 2011 Oct 15;124(Pt 20):3464-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.087080. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21984811 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of ultrasound stimulation on the cytoskeletal organization of chondrocytes seeded in three-dimensional matrices.Cells Tissues Organs. 2013;197(1):14-26. doi: 10.1159/000339772. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013. PMID: 22987069 Free PMC article.
-
Intermediate filaments take the heat as stress proteins.Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;20(2):79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.11.004. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20045331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fuchs E, Cleveland DW. A structural scaffolding of intermediate filaments in health and disease. Science. 1998;279:514–519. - PubMed
-
- Pekny M, Lane EB. Intermediate filaments and stress. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:2244–2254. - PubMed
-
- Green KJ, Simpson CL. Desmosomes: new perspectives on a classic. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:2499–2515. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann H, Bar H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:562–573. - PubMed
-
- Capetanaki Y, Bloch RJ, Kouloumenta A, Mavroidis M, Psarras S. Muscle intermediate filaments and their links to membranes and membranous organelles. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:2063–2076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

