Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition
- PMID: 18166352
- PMCID: PMC2194638
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.033
Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition
Abstract
Background & aims: A number of recent studies have implicated tissue hypoxia in both acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, particularly as they relate to mucosal surfaces lined by epithelial cells. In this context, a protective role for the transcriptional regulator hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) was shown through conditional deletion of epithelial HIF-1alpha in a murine model of colitis. Here, we hypothesized that pharmacologic activation of HIF would similarly provide a protective adaptation to murine colitic disease.
Methods: For these purposes, we used a novel prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) inhibitor (FG-4497) that readily stabilizes HIF-1alpha and subsequently drives the expression downstream of HIF target genes (eg, erythropoietin).
Results: Our results show that the FG-4497-mediated induction of HIF-1alpha provides an overall beneficial influence on clinical symptoms [weight loss, colon length, tissue tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha)] in murine trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) colitis, most likely because of their barrier protective function and wound healing during severe tissue hypoxia at the site of inflammation.
Conclusions: Taken together these findings emphasize the role of epithelial HIF-1alpha during inflammatory diseases in the colon and may provide the basis for a therapeutic use of PHD inhibitors in inflammatory mucosal disease.
Figures



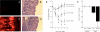

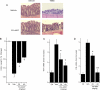

Comment in
-
Life in the gut without oxygen: adaptive mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease.Gastroenterology. 2008 Jan;134(1):346-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.049. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18166362 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Oral delivery of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor: AKB-4924 promotes localized mucosal healing in a mouse model of colitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Feb;21(2):267-75. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000277. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 25545377
-
Pharmacological HIF-1 stabilization promotes intestinal epithelial healing through regulation of α-integrin expression and function.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):G420-G438. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00192.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33470153
-
Contribution of epithelial innate immunity to systemic protection afforded by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition in murine colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2014 Jan;7(1):114-23. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.29. Epub 2013 May 22. Mucosal Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23695513 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and gastrointestinal disease.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Dec;85(12):1295-300. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0277-z. Epub 2007 Nov 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 18026919 Review.
-
Oxygen sensing in intestinal mucosal inflammation.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jan;468(1):77-84. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1722-4. Epub 2015 Jul 25. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26206140 Review.
Cited by
-
HIF-2α-dependent induction of miR-29a restrains TH1 activity during T cell dependent colitis.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 14;15(1):8042. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52113-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39271652 Free PMC article.
-
A Pro-Regenerative Supramolecular Prodrug Protects Against and Repairs Colon Damage in Experimental Colitis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(13):e2304716. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304716. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38247203 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between HIFs and tumor immune checkpoints: mechanism and therapy.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00836-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38165484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii promotes intestinal epithelial IL-18 production through activation of the HIF1α pathway.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 14;14:1298304. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1298304. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38163085 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting hypoxia-inducible factors: therapeutic opportunities and challenges.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Mar;23(3):175-200. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00848-6. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38123660 Review.
References
-
- Semenza GL, Agani F, Feldser D, Iyer N, Kotch L, Laughner E, Yu A. Hypoxia, HIF-1, and the pathophysiology of common human diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;475:123–30. - PubMed
-
- Comerford KM, Wallace TJ, Karhausen J, Louis NA, Montalto MC, Colgan SP. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent regulation of the multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3387–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DE013499-010003/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DE016191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- DE016191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DE013499/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK50189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060569-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189-06/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL60569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DE016191-010002/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

