Launching the T-cell-lineage developmental programme
- PMID: 18097446
- PMCID: PMC3131407
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2232
Launching the T-cell-lineage developmental programme
Abstract
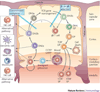
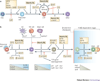
Multipotent blood progenitor cells enter the thymus and begin a protracted differentiation process in which they gradually acquire T-cell characteristics while shedding their legacy of developmental plasticity. Notch signalling and basic helix-loop-helix E-protein transcription factors collaborate repeatedly to trigger and sustain this process throughout the period leading up to T-cell lineage commitment. Nevertheless, the process is discontinuous with separately regulated steps that demand roles for additional collaborating factors. This Review discusses new evidence on the coordination of specification and commitment in the early T-cell pathway; effects of microenvironmental signals; the inheritance of stem-cell regulatory factors; and the ensemble of transcription factors that modulate the effects of Notch and E proteins, to distinguish individual stages and to polarize T-cell-lineage fate determination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T lineage progenitors: the earliest steps en route to T lymphocytes.Curr Opin Immunol. 2006 Apr;18(2):121-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2006.01.006. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16459068 Review.
-
Molecular dissection of prethymic progenitor entry into the T lymphocyte developmental pathway.J Immunol. 2007 Jul 1;179(1):421-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.421. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17579063
-
From stem cell to T cell: one route or many?Nat Rev Immunol. 2006 Feb;6(2):117-26. doi: 10.1038/nri1778. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16491136 Review.
-
Bone marrow-derived hemopoietic precursors commit to the T cell lineage only after arrival in the thymic microenvironment.J Immunol. 2007 Jan 15;178(2):858-68. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.2.858. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17202347
-
The functional relationship between hematopoietic stem cells and developing T lymphocytes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Apr;1370(1):36-44. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12995. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 26773328 Review.
Cited by
-
From murine to human nude/SCID: the thymus, T-cell development and the missing link.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:467101. doi: 10.1155/2012/467101. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22474479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic transformations of genome-wide epigenetic marking and transcriptional control establish T cell identity.Cell. 2012 Apr 13;149(2):467-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.056. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22500808 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Arrests DN2 to DN3 Pro T Cell Transition and Promotes Its Conversion to Thymic Dendritic Cells by Reciprocally Regulating Notch1 and Ikaros Signaling.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 5;11:898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00898. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582141 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors and target genes of pre-TCR signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(12):2305-21. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1864-8. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25702312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb repressor complex 2 regulates HOXA9 and HOXA10, activating ID2 in NK/T-cell lines.Mol Cancer. 2010 Jun 17;9:151. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-151. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20565746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayday AC, Pennington DJ. Key factors in the organized chaos of early T cell development. Nature Immunol. 2007;8:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MK. At the crossroads: diverse roles of early thymocyte transcriptional regulators. Immunol. Rev. 2006;209:191–211. - PubMed
-
- Petrie HT. Cell migration and the control of post-natal T-cell lymphopoiesis in the thymus. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg EV. Stepwise specification of lymphocyte developmental lineages. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2000;10:370–379. - PubMed
-
- Shortman K, et al. The linkage between T-cell and dendritic cell development in the mouse thymus. Immunol. Rev. 1998;165:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

