Functional analysis of human cytomegalovirus pUS28 mutants in infected cells
- PMID: 18089733
- PMCID: PMC2662737
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.83226-0
Functional analysis of human cytomegalovirus pUS28 mutants in infected cells
Abstract
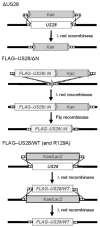
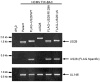
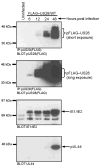
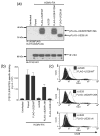
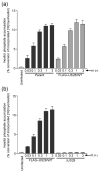
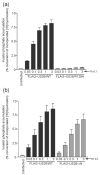
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-encoded viral G protein-coupled receptor pUS28 contributes to an array of biological effects, including cell migration and proliferation. Using FIX-BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome, derived from the HCMV clinical isolate VR1814) and lambda red recombination techniques, we generated HCMV recombinants expressing amino-terminally FLAG-tagged versions of wild-type pUS28 (FLAG-US28/WT), G-protein coupling deficient pUS28 (FLAG-US28/R129A) and chemokine-binding domain deficient pUS28 (FLAG-US28/DeltaN). Infection with the FLAG-US28/R129A virus failed to induce inositol phosphate accumulation, indicating that G-protein coupling is essential for pUS28 signalling to phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) during HCMV infection. The FLAG-US28/DeltaN virus induced about 80 % of the level of PLC-beta signalling induced by the FLAG-US28/WT virus, demonstrating that the N-terminal chemokine-binding domain is not required for pUS28-induced PLC-beta signalling in infected cells. The data presented here are the first to describe the functional analyses of several key pUS28 mutants in HCMV-infected cells. Elucidating the mechanisms by which pUS28 signals during infection will provide important insights into HCMV pathogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Constitutive inositol phosphate formation in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts is due to expression of the chemokine receptor homologue pUS28.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(8):4489-501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4489-4501.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12663756 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus G protein-coupled receptor US28 promotes latency by attenuating c-fos.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 29;116(5):1755-1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816933116. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30647114 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxy-terminal tail of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) US28 regulates both chemokine-independent and chemokine-dependent signaling in HCMV-infected cells.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):10016-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00354-09. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19605482 Free PMC article.
-
US28: HCMV's Swiss Army Knife.Viruses. 2018 Aug 20;10(8):445. doi: 10.3390/v10080445. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30127279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus US28: a functionally selective chemokine binding receptor.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Nov;9(5):548-56. doi: 10.2174/187152609789105696. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19594424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delivery of US28 by incoming HCMV particles rapidly attenuates Akt activity to suppress HCMV lytic replication in monocytes.Sci Signal. 2024 Aug 27;17(851):eadn8727. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adn8727. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 39190708 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus US28 regulates cellular EphA2 to maintain viral latency.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 28;8(43):eadd1168. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add1168. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36288299 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a Lambda-RED Recombination Method for Rapid Gene Deletion in Human Cytomegalovirus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10558. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910558. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638896 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Studying the Function of Cytomegalovirus GPCRs.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2244:159-197. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1111-1_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33555587
-
The constitutive activity of the viral-encoded G protein-coupled receptor US28 supports a complex signalling network contributing to cancer development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Aug 28;48(4):1493-1504. doi: 10.1042/BST20190988. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32779712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennett TA, Maestas DC, Prossnitz ER. Arrestin binding to the G protein-coupled N-formyl peptide receptor is regulated by the conserved “DRY” sequence. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:24590–24594. - PubMed
-
- Bodaghi B, Jones TR, Zipeto D, Vita C, Sun L, Laurent L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Virelizier JL, Michelson S. Chemokine sequestration by viral chemoreceptors as a novel viral escape strategy: withdrawal of chemokines from the environment of cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Exp Med. 1998;188:855–866. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boomker JM, Verschuuren EA, Brinker MG, de Leij LF, The TH, Harmsen MC. Kinetics of US28 gene expression during active human cytomegalovirus infection in lung-transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1552–1556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

