Pseudomonas aeruginosa PqsA is an anthranilate-coenzyme A ligase
- PMID: 18083812
- PMCID: PMC2238192
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01140-07
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PqsA is an anthranilate-coenzyme A ligase
Abstract
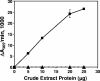
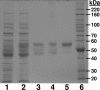
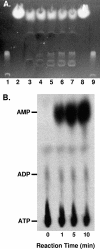
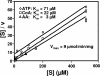
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic human pathogen which relies on several intercellular signaling systems for optimum population density-dependent regulation of virulence genes. The Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) is a 3-hydroxy-4-quinolone with a 2-alkyl substitution which is synthesized by the condensation of anthranilic acid with a 3-keto-fatty acid. The pqsABCDE operon has been identified as being necessary for PQS production, and the pqsA gene encodes a predicted protein with homology to acyl coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) ligases. In order to elucidate the first step of the 4-quinolone synthesis pathway in P. aeruginosa, we have characterized the function of the pqsA gene product. Extracts prepared from Escherichia coli expressing PqsA were shown to catalyze the formation of anthraniloyl-CoA from anthranilate, ATP, and CoA. The PqsA protein was purified as a recombinant His-tagged polypeptide, and this protein was shown to have anthranilate-CoA ligase activity. The enzyme was active on a variety of aromatic substrates, including benzoate and chloro and fluoro derivatives of anthranilate. Inhibition of PQS formation in vivo was observed for the chloro- and fluoroanthranilate derivatives, as well as for several analogs which were not PqsA enzymatic substrates. These results indicate that the PqsA protein is responsible for priming anthranilate for entry into the PQS biosynthetic pathway and that this enzyme may serve as a useful in vitro indicator for potential agents to disrupt quinolone signaling in P. aeruginosa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure of PqsD, a Pseudomonas quinolone signal biosynthetic enzyme, in complex with anthranilate.Biochemistry. 2009 Sep 15;48(36):8644-55. doi: 10.1021/bi9009055. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19694421 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of the N-Terminal Domain of PqsA in Complex with Anthraniloyl- and 6-Fluoroanthraniloyl-AMP: Substrate Activation in Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS) Biosynthesis.Chembiochem. 2017 Oct 18;18(20):2045-2055. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201700374. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Chembiochem. 2017. PMID: 28834007
-
Growth phase-differential quorum sensing regulation of anthranilate metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Mol Cells. 2011 Jul;32(1):57-65. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-2322-6. Epub 2011 May 23. Mol Cells. 2011. PMID: 21614486 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological and clinical significance of quorum sensing alkylquinolones: current analytical and bioanalytical methods for their quantification.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Jul;413(18):4599-4618. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03356-x. Epub 2021 May 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33959788 Review.
-
Spatiotemporal Distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alkyl Quinolones under Metabolic and Competitive Stress.mSphere. 2020 Jul 22;5(4):e00426-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00426-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32699119 Free PMC article.
-
Static Growth Promotes PrrF and 2-Alkyl-4(1H)-Quinolone Regulation of Type VI Secretion Protein Expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2020 Nov 19;202(24):e00416-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00416-20. Print 2020 Nov 19. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 33020221 Free PMC article.
-
A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Anthranilyl-CoA Synthetase PqsA for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0276421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02764-21. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35856709 Free PMC article.
-
The Small RNA AmiL Regulates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0221121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02211-21. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35262393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altenschmidt, U., and G. Fuchs. 1992. Novel aerobic 2-aminobenzoate metabolism. Purification and characterization of 2-aminobenzoate-CoA ligase, localisation of the gene on a 8-kbp plasmid, and cloning and sequencing of the gene from a denitrifying Pseudomonas sp. Eur. J. Biochem. 205721-727. - PubMed
-
- Auburger, G., and J. Winter. 1992. Purification and characterization of benzoyl-CoA ligase from a syntrophic, benzoate-degrading, anaerobic mixed culture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37789-795. - PubMed
-
- Babbitt, P. C., G. L. Kenyon, B. M. Martin, H. Charest, M. Slyvestre, J. D. Scholten, K. H. Chang, P. H. Liang, and D. Dunaway-Mariano. 1992. Ancestry of the 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase: analysis of amino acid sequence identities among families of acyl:adenyl ligases, enoyl-CoA hydratases/isomerases, and acyl-CoA thioesterases. Biochemistry 315594-5604. - PubMed
-
- Bains, J., and M. J. Boulanger. 2007. Biochemical and structural characterization of the paralogous benzoate CoA ligases from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400: defining the entry point into the novel benzoate oxidation (box) pathway. J. Mol. Biol. 373965-977. - PubMed
-
- Bandara, M. B., H. Zhu, P. R. Sankaridurg, and M. D. Willcox. 2006. Salicylic acid reduces the production of several potential virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with microbial keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 474453-4460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

