HIV-1 accessory proteins VPR and Vif modulate antiviral response by targeting IRF-3 for degradation
- PMID: 18082865
- PMCID: PMC2312338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.10.042
HIV-1 accessory proteins VPR and Vif modulate antiviral response by targeting IRF-3 for degradation
Abstract
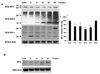
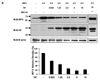
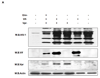
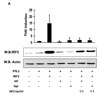
The activation of IRF-3 during the early stages of viral infection is critical for the initiation of the antiviral response; however the activation of IRF-3 in HIV-1 infected cells has not yet been characterized. We demonstrate that the early steps of HIV-1 infection do not lead to the activation and nuclear translocation of IRF-3; instead, the relative levels of IRF-3 protein are decreased due to the ubiquitin-associated proteosome degradation. Addressing the molecular mechanism of this effect we show that the degradation is independent of HIV-1 replication and that virion-associated accessory proteins Vif and Vpr can independently degrade IRF-3. The null mutation of these two genes reduced the capacity of the HIV-1 virus to down modulate IRF-3 levels. The degradation was associated with Vif- and Vpr-mediated ubiquitination of IRF-3 and was independent of the activation of IRF-3. N-terminal lysine residues were shown to play a critical role in the Vif- and Vpr-mediated degradation of IRF-3. These data implicate Vif and Vpr in the disruption of the initial antiviral response and point to the need of HIV-1 to circumvent the antiviral response during the very early phase of replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures










Similar articles
-
The HIV-1 Vif protein mediates degradation of Vpr and reduces Vpr-induced cell cycle arrest.DNA Cell Biol. 2008 May;27(5):267-77. doi: 10.1089/dna.2007.0707. DNA Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18462066
-
HIV-1 Vpu accessory protein induces caspase-mediated cleavage of IRF3 transcription factor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35102-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597062. Epub 2014 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25352594 Free PMC article.
-
Accessories to the crime: recent advances in HIV accessory protein biology.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2009 Feb;6(1):36-42. doi: 10.1007/s11904-009-0006-z. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2009. PMID: 19149995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual regulation of L-selectin (CD62L) by HIV-1: Enhanced expression by Vpr in contrast with cell-surface down-modulation by Nef and Vpu.Virology. 2018 Oct;523:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.07.031. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Virology. 2018. PMID: 30119013
-
HIV-1 accessory proteins--ensuring viral survival in a hostile environment.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Jun 12;3(6):388-98. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.04.008. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18541215 Review.
Cited by
-
The subversion of toll-like receptor signaling by bacterial and viral proteases during the development of infectious diseases.Mol Aspects Med. 2022 Dec;88:101143. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101143. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Mol Aspects Med. 2022. PMID: 36152458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vpu-deficient HIV strains stimulate innate immune signaling responses in target cells.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(16):8499-506. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00424-12. Epub 2012 May 30. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22647704 Free PMC article.
-
Vpr Is a VIP: HIV Vpr and Infected Macrophages Promote Viral Pathogenesis.Viruses. 2020 Jul 27;12(8):809. doi: 10.3390/v12080809. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32726944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by type I interferons: impact of cell-to-cell viral transfer.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(20):10527-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01235-09. Epub 2009 Aug 12. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19706714 Free PMC article.
-
HIV blocks Type I IFN signaling through disruption of STAT1 phosphorylation.Innate Immun. 2018 Nov;24(8):490-500. doi: 10.1177/1753425918803674. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Innate Immun. 2018. PMID: 30282499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124(4):783–801. - PubMed
-
- Au WC, Yeow WS, Pitha PM. Analysis of functional domains of interferon regulatory factor 7 and its association with IRF-3. Virology. 2001;280(2):273–282. - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Fruh K. Viral modulators of cullin RING ubiquitin ligases: culling the host defense. Sci STKE 2006. 2006;(335):pe21. - PubMed
-
- Basler CF, Garcia-Sastre A. Viruses and the type I interferon antiviral system: induction and evasion. Int Rev Immunol. 2002;21(4–5):305–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

