Cx43 hemichannels and gap junction channels in astrocytes are regulated oppositely by proinflammatory cytokines released from activated microglia
- PMID: 18077690
- PMCID: PMC6673621
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2042-07.2007
Cx43 hemichannels and gap junction channels in astrocytes are regulated oppositely by proinflammatory cytokines released from activated microglia
Abstract
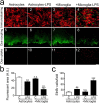
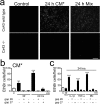
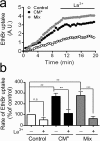
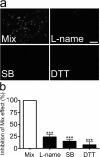
Astrocytes have a role in maintaining normal neuronal functions, some of which depend on connexins, protein subunits of gap junction channels and hemichannels. Under inflammatory conditions, microglia release cytokines, including interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, that reduce intercellular communication via gap junctions. Now, we demonstrate that either conditioned medium harvested from activated microglia or a mixture of these two cytokines enhances the cellular exchange with the extracellular milieu via Cx43 hemichannels. These changes in membrane permeability were not detected in astrocytes cultured from Cx43 knock-out mice and were abrogated by connexin hemichannel blockers, including La3+, mimetic peptides, and niflumic acid. Both the reduction in gap junctional communication and the increase in membrane permeability were mediated by a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. However, the increase in membrane permeability, but not the gap junction inhibition, was rapidly reversed by the sulfhydryl reducing agent dithiothreitol, indicating that final regulatory mechanisms are different. Treatment with proinflammatory cytokines reduced the total and cell surface Cx43 levels, suggesting that the increase in membrane permeability was attributable to an increase in hemichannels activity. Indeed, unitary events of approximately 220 pS corresponding to Cx43 hemichannels were much more frequent in astrocytes treated with microglia conditioned medium than under control conditions. Finally, the effect of cytokines enhanced the uptake and reduced the intercellular diffusion of glucose, which might explain changes in the metabolic status of astrocytes under inflammatory conditions. Accordingly, this opposite regulation may affect glucose trafficking and certainly will modify the metabolic status of astrocytes involved in brain inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of astrocytic connexin-43, hemichannels, and gap junctions in oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury induced neuroinflammation and the possible regulatory mechanisms of salvianolic acid B and carbenoxolone.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Mar 27;15(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1127-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29587860 Free PMC article.
-
ATP and glutamate released via astroglial connexin 43 hemichannels mediate neuronal death through activation of pannexin 1 hemichannels.J Neurochem. 2011 Sep;118(5):826-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07210.x. Epub 2011 Mar 7. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21294731 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory cytokines released from microglia inhibit gap junctions in astrocytes: potentiation by beta-amyloid.FASEB J. 2006 Mar;20(3):494-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4297fje. Epub 2006 Jan 19. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16423877
-
Connexin and pannexin hemichannels in inflammatory responses of glia and neurons.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.042. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22975435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptides and peptide-derived molecules targeting the intracellular domains of Cx43: gap junctions versus hemichannels.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:491-505. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.050. Epub 2013 May 7. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23664811 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Astrocytes in Parkinson's Disease : Astrocytes in Parkinson's Disease.Adv Neurobiol. 2024;39:319-343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-64839-7_13. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39190081 Review.
-
Connexin 43 Modulation in Human Chondrocytes, Osteoblasts and Cartilage Explants: Implications for Inflammatory Joint Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 5;25(15):8547. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158547. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126115 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical functions of adhesion proteins in inflammation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):C505-C515. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00292.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38981610 Review.
-
Connexin channels and hemichannels are modulated differently by charge reversal at residues forming the intracellular pocket.Biol Res. 2024 May 23;57(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00501-5. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38783330 Free PMC article.
-
Astroglial connexin 43 is a novel therapeutic target for chronic multiple sclerosis model.Sci Rep. 2024 May 13;14(1):10877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61508-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38740862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badger AM, Cook MN, Lark MW, Newman-Tarr TM, Swift BA, Nelson AH, Barone FC, Kumar S. SB 203580 inhibits p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, nitric oxide production, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in bovine cartilage-derived chondrocytes. J Immunol. 1998;161:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Bao L, Locovei S, Dahl G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Battelino T, Goto M, Krzisnik C, Zeller WP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha alters glucose metabolism in suckling rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1999;133:583–589. - PubMed
-
- Blomstrand F, Giaume C. Kinetics of endothelin-induced inhibition and glucose permeability of astrocyte gap junctions. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:996–1003. - PubMed
-
- Boone E, Vandevoorde V, De Wilde G, Haegeman G. Activation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and p38 MAPK by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is mediated through the death domain of the 55-kDa TNF receptor. FEBS Lett. 1998;441:275–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
