Treatment with CD20-specific antibody prevents and reverses autoimmune diabetes in mice
- PMID: 18060033
- PMCID: PMC2096456
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32405
Treatment with CD20-specific antibody prevents and reverses autoimmune diabetes in mice
Abstract
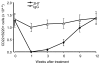
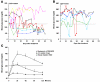
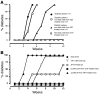
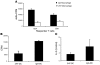
The precise roles of B cells in promoting the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes remain undefined. Here, we demonstrate that B cell depletion in mice can prevent or delay diabetes, reverse diabetes after frank hyperglycemia, and lead to the development of cells that suppress disease. To determine the efficacy and potential mechanism of therapeutic B cell depletion, we generated a transgenic NOD mouse expressing human CD20 (hCD20) on B cells. A single cycle of treatment with an antibody specific for hCD20 temporarily depleted B cells and significantly delayed and/or reduced the onset of diabetes. Furthermore, disease established to the point of clinical hyperglycemia could be reversed in over one-third of diabetic mice. Why B cell depletion is therapeutic for a variety of autoimmune diseases is unclear, although effects on antibodies, cytokines, and antigen presentation to T cells are thought to be important. In B cell-depleted NOD mice, we identified what we believe is a novel mechanism by which B cell depletion may lead to long-term remission through expansion of Tregs and regulatory B cells. Our results demonstrate clinical efficacy even in established disease and identify mechanisms for therapeutic action that will guide design and evaluation of parallel studies in patients.
Figures

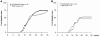
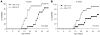
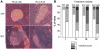

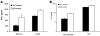
Comment in
-
B cell depletion: a novel therapy for autoimmune diabetes?J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3642-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI34236. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060022 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
B cell depletion: a novel therapy for autoimmune diabetes?J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3642-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI34236. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18060022 Free PMC article.
-
B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2863-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.2863. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18292508
-
Transient B-cell depletion with anti-CD20 in combination with proinsulin DNA vaccine or oral insulin: immunologic effects and efficacy in NOD mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e54712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054712. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405091 Free PMC article.
-
B cells and type 1 diabetes ...in mice and men.Immunol Lett. 2014 Aug;160(2):128-32. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24472603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Change you can B(cell)eive in: recent progress confirms a critical role for B cells in type 1 diabetes.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2009 Aug;16(4):293-8. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e32832e06a7. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2009. PMID: 19502979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered BCR signalling quality predisposes to autoimmune disease and a pre-diabetic state.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 1;31(15):3363-74. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.169. Epub 2012 Jun 22. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22728826 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of Activated Peripheral Blood Memory B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Impact of B Cell Depletion Therapy, and Biomarkers of Response.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128269. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047509 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical immunologic interventions for the treatment of type 1 diabetes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Aug 1;2(8):a007716. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007716. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 22908194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel autoantibodies to the β-cell surface epitopes of ZnT8 in patients progressing to type-1 diabetes.J Autoimmun. 2021 Aug;122:102677. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102677. Epub 2021 Jun 12. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 34130115 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of BAFF inhibition and B-cell depletion in non-obese diabetic mice as a spontaneous model for Sjögren's disease.RMD Open. 2024 Aug 28;10(3):e004112. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004112. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 39209370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noorchashm H., et al. B-cells are required for the initiation of insulitis and sialitis in nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1997;46:941–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

