Lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 mediates amyloid-beta-mediated cell death of cerebrovascular cells
- PMID: 18055545
- PMCID: PMC2111121
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070050
Lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 mediates amyloid-beta-mediated cell death of cerebrovascular cells
Abstract
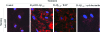
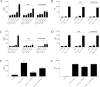
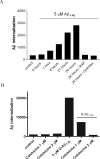
Inefficient clearance of A beta, caused by impaired blood-brain barrier crossing into the circulation, seems to be a major cause of A beta accumulation in the brain of late-onset Alzheimer's disease patients and hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis Dutch type. We observed association of receptor for advanced glycation end products, CD36, and low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) with cerebral amyloid angiopathy in both Alzheimer's disease and hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis Dutch type brains and increased low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1) expression by perivascular cells in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. We investigated if these A beta receptors are involved in A beta internalization and in A beta-mediated cell death of human cerebrovascular cells and astrocytes. Expression of both the LRP-1 and LDLR by human brain pericytes and leptomeningeal smooth muscle cells, but not by astrocytes, increased on incubation with A beta. Receptor-associated protein specifically inhibited A beta-mediated up-regulation of LRP-1, but not of LDLR, and receptor-associated protein also decreased A beta internalization and A beta-mediated cell death. We conclude that especially LRP-1 and, to a minor extent, LDLR are involved in A beta internalization by and A beta-mediated cell death of cerebral perivascular cells. Although perivascular cells may adapt their A beta internalization capacity to the levels of A beta present, saturated LRP-1/LDLR-mediated uptake of A beta results in degeneration of perivascular cells.
Figures
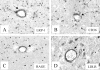
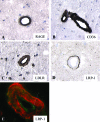
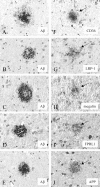
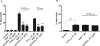
Similar articles
-
RAGE (yin) versus LRP (yang) balance regulates alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide clearance through transport across the blood-brain barrier.Stroke. 2004 Nov;35(11 Suppl 1):2628-31. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000143452.85382.d1. Epub 2004 Sep 30. Stroke. 2004. PMID: 15459432
-
Amyloid-β protein modulates the perivascular clearance of neuronal apolipoprotein E in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011 May;118(5):699-712. doi: 10.1007/s00702-010-0572-7. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011. PMID: 21210284
-
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion alters amyloid-β transport related proteins in the cortical blood vessels of Alzheimer's disease model mouse.Brain Res. 2019 Nov 15;1723:146379. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146379. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31415766
-
The role of the cell surface LRP and soluble LRP in blood-brain barrier Abeta clearance in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(16):1601-5. doi: 10.2174/138161208784705487. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18673201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid β in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-Dutch type.Rev Neurosci. 2014;25(5):641-51. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2014-0008. Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24870607 Review.
Cited by
-
Statins Inhibit Fibrillary β-Amyloid Induced Inflammation in a Model of the Human Blood Brain Barrier.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157483. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27309956 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in amyloid-β 1-42-induced shedding of the pericyte proteoglycan NG2.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014 Jul;73(7):684-92. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000084. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24918635 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Jul;18(7):419-434. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.48. Epub 2017 May 18. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28515434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier-associated pericytes internalize and clear aggregated amyloid-β42 by LRP1-dependent apolipoprotein E isoform-specific mechanism.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Oct 19;13(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0286-0. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30340601 Free PMC article.
-
Brain microvascular pericytes are immunoactive in culture: cytokine, chemokine, nitric oxide, and LRP-1 expression in response to lipopolysaccharide.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Oct 13;8:139. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-139. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21995440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Clearing the brain’s amyloid cobwebs. Neuron. 2001;32:177–180. - PubMed
-
- Ghiso J, Frangione B. Amyloidosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54:1539–1551. - PubMed
-
- Davis-Salinas J, Saporito-Irwin SM, Cotman CW, Van Nostrand WE. Amyloid beta-protein induces its own production in cultured degenerating cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells. J Neurochem. 1995;65:931–934. - PubMed
-
- Van Nostrand WE, Melchor JP, Ruffini L. Pathologic amyloid beta-protein cell surface fibril assembly on cultured human cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells. J Neurochem. 1998;70:216–223. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek MM, de Waal RM, Schipper JJ, Van Nostrand WE. Rapid degeneration of cultured human brain pericytes by amyloid beta protein. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1135–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

