Binding MOAD, a high-quality protein-ligand database
- PMID: 18055497
- PMCID: PMC2238910
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm911
Binding MOAD, a high-quality protein-ligand database
Abstract
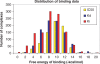
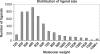
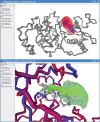
Binding MOAD (Mother of All Databases) is a database of 9836 protein-ligand crystal structures. All biologically relevant ligands are annotated, and experimental binding-affinity data is reported when available. Binding MOAD has almost doubled in size since it was originally introduced in 2004, demonstrating steady growth with each annual update. Several technologies, such as natural language processing, help drive this constant expansion. Along with increasing data, Binding MOAD has improved usability. The website now showcases a faster, more featured viewer to examine the protein-ligand structures. Ligands have additional chemical data, allowing for cheminformatics mining. Lastly, logins are no longer necessary, and Binding MOAD is freely available to all at http://www.BindingMOAD.org.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring protein-ligand recognition with Binding MOAD.J Mol Graph Model. 2006 May;24(6):414-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2005.08.002. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Mol Graph Model. 2006. PMID: 16168689
-
Updates to Binding MOAD (Mother of All Databases): Polypharmacology Tools and Their Utility in Drug Repurposing.J Mol Biol. 2019 Jun 14;431(13):2423-2433. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.05.024. Epub 2019 May 22. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31125569 Free PMC article.
-
Recent improvements to Binding MOAD: a resource for protein-ligand binding affinities and structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D465-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1088. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25378330 Free PMC article.
-
The use of protein-ligand interaction fingerprints in docking.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008 May;11(3):356-64. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008. PMID: 18428089 Review.
-
CHARMM-GUI PDB manipulator for advanced modeling and simulations of proteins containing nonstandard residues.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2014;96:235-65. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 25443960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Text mining improves prediction of protein functional sites.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032171. Epub 2012 Feb 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22393388 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting locations of cryptic pockets from single protein structures using the PocketMiner graph neural network.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 1;14(1):1177. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36699-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36859488 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening using molecular simulations.Proteins. 2011 Jun;79(6):1940-51. doi: 10.1002/prot.23018. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Proteins. 2011. PMID: 21491494 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing protein-ligand interaction scoring functions with the CASF-2013 benchmark.Nat Protoc. 2018 Apr;13(4):666-680. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.114. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29517771
-
Prediction of trypsin/molecular fragment binding affinities by free energy decomposition and empirical scores.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012 May;26(5):647-59. doi: 10.1007/s10822-012-9567-9. Epub 2012 Apr 4. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2012. PMID: 22476578
References
-
- Hu L, Benson ML, Smith RD, Lerner MG, Carlson HA. Binding MOAD (Mother Of All Databases) Prot. Struct. Func. Bioinf. 2005;60:333–340. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Fang X, Lu Y, Yang CY, Wang S. The PDBbind Database: methodologies and updates. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:4111–4119. - PubMed
-
- Roche O, Kiyama R, Brooks CL. Ligand-protein database: linking protein-ligand complex structures to binding data. J. Med. Chem. 2001;44:3592–3598. - PubMed
-
- Hendlich M, Bergner A, Gunther J, Klebe G. Relibase: design and development of a database for comprehensive analysis of protein-ligand interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;326:607–620. - PubMed

