NK-cell activation and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity induced by rituximab-coated target cells is inhibited by the C3b component of complement
- PMID: 18024795
- PMCID: PMC2214766
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-074716
NK-cell activation and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity induced by rituximab-coated target cells is inhibited by the C3b component of complement
Abstract
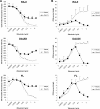
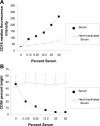
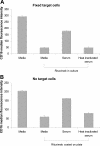
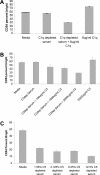
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement fixation both appear to play a role in mediating antitumor effects of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), including rituximab. We evaluated the relationship between rituximab-induced complement fixation, natural killer (NK)-cell activation, and NK cell-mediated ADCC. Down-modulation of NK- cell CD16 and NK-cell activation induced by rituximab-coated target cells was blocked by human serum but not heat-inactivated serum. This inhibition was also observed in the absence of viable target cells. C1q and C3 in the serum were required for these inhibitory effects, while C5 was not. An antibody that stabilizes C3b on the target cell surface enhanced the inhibition of NK-cell activation induced by rituximab-coated target cells. Binding of NK cells to rituximab-coated plates through CD16 was inhibited by the fixation of complement. C5-depleted serum blocked NK cell-mediated ADCC. These data suggest that C3b deposition induced by rituximab-coated target cells inhibits the interaction between the rituximab Fc and NK-cell CD16, thereby limiting the ability of rituximab-coated target cells to induce NK activation and ADCC. Further studies are needed to define in more detail the impact of complement fixation on ADCC, and whether mAbs that fail to fix complement will be more effective at mediating ADCC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GA101 induces NK-cell activation and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity more effectively than rituximab when complement is present.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Nov;54(11):2500-5. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.781169. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23452151 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of interleukin-18 on natural killer cells: costimulation of activation through Fc receptors for immunoglobulin.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Jun;62(6):1073-82. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1403-0. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23604103 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody with enhanced affinity for CD16 activates NK cells at lower concentrations and more effectively than rituximab.Blood. 2006 Oct 15;108(8):2648-54. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-020057. Epub 2006 Jul 6. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16825493 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations of Antibody Geometric Constraints on NK Cell Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 30;11:1635. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01635. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer (NK): dendritic cell (DC) cross talk induced by therapeutic monoclonal antibody triggers tumor antigen-specific T cell immunity.Immunol Res. 2011 Aug;50(2-3):248-54. doi: 10.1007/s12026-011-8231-0. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 21717064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GA101 induces NK-cell activation and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity more effectively than rituximab when complement is present.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Nov;54(11):2500-5. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.781169. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23452151 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy for B-cell lymphoma: current status and prospective advances.Front Immunol. 2012 Jan 24;3:3. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00003. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22566889 Free PMC article.
-
Fractionated subcutaneous rituximab is well-tolerated and preserves CD20 expression on tumor cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Haematologica. 2010 Feb;95(2):329-32. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.012484. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 19679883 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of immunomonitoring of antibody‑dependent cellular cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma cells using whole blood.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 Jun;63(6):559-69. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1534-y. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24658837 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of membrane complement regulators improves complement-dependent effector functions of therapeutic anticancer antibodies targeting leukemic cells.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Jan 22;4(3):e979688. doi: 10.4161/2162402X.2014.979688. eCollection 2015 Mar. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 25949896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Meerten T, van Rijn RS, Hol S, Hagenbeek A, Ebeling SB. Complement-induced cell death by rituximab depends on CD20 expression level and acts complementary to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4027–4035. - PubMed
-
- Golay J, Zaffaroni L, Vaccari T, et al. Biologic response of B lymphoma cells to anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in vitro: CD55 and CD59 regulate complement-mediated cell lysis. Blood. 2000;95:3900–3908. - PubMed
-
- Harjunpaa A, Junnikkala S, Meri S. Rituximab (anti-CD20) therapy of B-cell lymphomas: direct complement killing is superior to cellular effector mechanisms. Scand J Immunol. 2000;51:634–641. - PubMed
-
- Weng WK, Levy R. Expression of complement inhibitors CD46, CD55, and CD59 on tumor cells does not predict clinical outcome after rituximab treatment in follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2001;98:1352–1357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

