Nkx2.2 regulates cell fate choice in the enteroendocrine cell lineages of the intestine
- PMID: 18022152
- PMCID: PMC2238176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.09.047
Nkx2.2 regulates cell fate choice in the enteroendocrine cell lineages of the intestine
Abstract
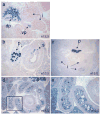
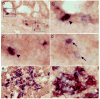
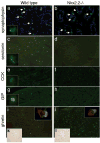
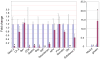
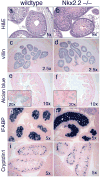
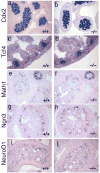
Nkx2.2 is a homeodomain-containing transcription factor essential for pancreatic islet cell specification. In this study we investigate the role of Nkx2.2 within the small intestine. We have determined that Nkx2.2 is expressed at the onset of intestinal epithelial cell differentiation in specific intestinal cell populations, including a subset of enteroendocrine cells. Similar to its role in the pancreatic islet, Nkx2.2 regulates cell fate choices within the intestinal enteroendocrine population; in the Nkx2.2 null mice, several hormone-producing enteroendocrine cell populations are absent or reduced and the ghrelin-producing cell population is upregulated. The remaining intestinal cell populations, including the paneth cells, goblet cells, and enterocytes appear to be unaffected by the loss of Nkx2.2. Furthermore, similar to the pancreatic islet, Nkx2.2 appears to function upstream of Pax6 in regulating intestinal cell fates; Pax6 mRNA and protein expression is decreased in the Nkx2.2 null mice. These studies identify a novel role for Nkx2.2 in intestinal endocrine cell development and reveal the regulatory similarities between cell type specification in the pancreatic islet and in the enteroendocrine population of the intestine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The novel enterochromaffin marker Lmx1a regulates serotonin biosynthesis in enteroendocrine cell lineages downstream of Nkx2.2.Development. 2016 Jul 15;143(14):2616-28. doi: 10.1242/dev.130682. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Development. 2016. PMID: 27287799 Free PMC article.
-
Homeodomain transcription factor NKX2.2 functions in immature cells to control enteroendocrine differentiation and is expressed in gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009 Mar;16(1):267-79. doi: 10.1677/ERC-08-0127. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009. PMID: 18987169
-
Nkx2.2 and Arx genetically interact to regulate pancreatic endocrine cell development and endocrine hormone expression.Dev Biol. 2011 Nov 1;359(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21856296 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Development and differentiation of gut endocrine cells.Endocrinology. 2004 Jun;145(6):2639-44. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0051. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15044355 Review.
-
Differential use of the Nkx2.2 NK2 domain in developing pancreatic islets and neurons.Genes Dev. 2023 Jun 1;37(11-12):451-453. doi: 10.1101/gad.350895.123. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 37399332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel group of secretory cells regulates development of the immature intestinal stem cell niche through repression of the main signaling pathways driving proliferation.Dev Biol. 2019 Dec 1;456(1):47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31398318 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of cell-fate decision landscapes by estimating transcription factor dynamics.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Jun 22;3(7):100512. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100512. eCollection 2023 Jul 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 37533652 Free PMC article.
-
ISX-9 manipulates endocrine progenitor fate revealing conserved intestinal lineages in mouse and human organoids.Mol Metab. 2020 Apr;34:157-173. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.01.012. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32180555 Free PMC article.
-
NK2 homeobox gene cluster: Functions and roles in human diseases.Genes Dis. 2022 Oct 11;10(5):2038-2048. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.001. eCollection 2023 Sep. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37492711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin is dispensable for embryonic pancreatic islet development and differentiation.Regul Pept. 2009 Oct 9;157(1-3):51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.02.013. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Regul Pept. 2009. PMID: 19268691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren U, et al. Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature. 1997;385:257–60. - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist A, et al. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature. 1999;400:877–81. - PubMed
-
- Braunstein EM, et al. Villin: A marker for development of the epithelial pyloric border. Dev Dyn. 2002;224:90–102. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, et al. A homeodomain protein code specifies progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in the ventral neural tube. Cell. 2000;101:435–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

