Telomerase activity is required for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 18008008
- PMCID: PMC2075478
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32369
Telomerase activity is required for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
Abstract
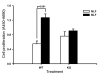
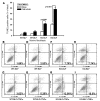
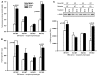
In addition to its well-known expression in the germline and in cells of certain cancers, telomerase activity is induced in lung fibrosis, although its role in this process is unknown. To identify the pathogenetic importance of telomerase in lung fibrosis, we examined the effects of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) deficiency in a murine model of pulmonary injury. TERT-deficient mice showed significantly reduced lung fibrosis following bleomycin (BLM) insult. This was accompanied by a significant reduction in expression of lung alpha-SMA, a marker of myofibroblast differentiation. Furthermore, lung fibroblasts isolated from BLM-treated TERT-deficient mice showed significantly decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis rates compared with cells isolated from control mice. Transplantation of WT BM into TERT-deficient mice restored BLM-induced lung telomerase activity and fibrosis to WT levels. Conversely, transplantation of BM from TERT-deficient mice into WT recipients resulted in reduced telomerase activity and fibrosis. These findings suggest that induction of telomerase in injured lungs may be caused by BM-derived cells, which appear to play an important role in pulmonary fibrosis. Moreover, TERT induction is associated with increased survival of lung fibroblasts, which favors the development of fibrosis instead of injury resolution.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of telomerase activity in rat lung fibroblasts.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002 May;26(5):534-40. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.26.5.4668. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11970904
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase ameliorates lung fibrosis by protecting alveolar epithelial cells against senescence.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 31;294(22):8861-8871. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006615. Epub 2019 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31000627 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase and telomere length in pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):260-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0514OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telomerase deficiency does not alter bleomycin-induced fibrosis in mice.Exp Lung Res. 2012 Apr;38(3):124-34. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2012.658148. Exp Lung Res. 2012. PMID: 22394286 Free PMC article.
-
Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: From biological mechanisms to counteractions.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Jul;97:122-30. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 May 8. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 25959210 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone Marrow CD11c+ Cell-Derived Amphiregulin Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis.J Immunol. 2016 Jul 1;197(1):303-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502479. Epub 2016 May 20. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27206766 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPβ-Thr217 phosphorylation signaling contributes to the development of lung injury and fibrosis in mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025497. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998664 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2009 Jul;175(1):3-16. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.081170. Epub 2009 Jun 4. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19497999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease.Nat Med. 2012 Jul 6;18(7):1028-40. doi: 10.1038/nm.2807. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22772564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-4 is proangiogenic in the lung under hypoxic conditions.J Immunol. 2009 May 1;182(9):5469-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0713347. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19380795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greider C.W. Telomere length regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:337–365. - PubMed
-
- Counter C.M., et al. Telomerase activity is restored in human cells by ectopic expression of hTERT (hEST2), the catalytic subunit of telomerase. Oncogene. 1998;16:1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Feng J., et al. The RNA component of human telomerase. Science. 1995;269:1236–1241. - PubMed
-
- Blasco M.A., Gasser S.M., Lingner J. Telomeres and telomerase. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2353–2359. - PubMed
-
- Koyanagi Y., et al. Telomerase activity is down regulated via decreases in hTERT mRNA but not TEP1 mRNA or hTERC during the differentiation of leukemic cells. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:773–778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

