Novel pro- and anti-recombination activities of the Bloom's syndrome helicase
- PMID: 18003860
- PMCID: PMC2081975
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1609007
Novel pro- and anti-recombination activities of the Bloom's syndrome helicase
Abstract
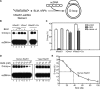
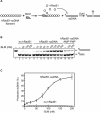
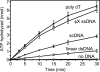
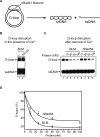
Bloom's syndrome (BS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a strong cancer predisposition. The defining feature of BS is extreme genome instability. The gene mutated in Bloom's syndrome, BLM, encodes a DNA helicase (BLM) of the RecQ family. BLM plays a role in homologous recombination; however, its exact function remains controversial. Mutations in the BLM cause hyperrecombination between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes, indicating an anti-recombination role. Conversely, other data show that BLM is required for recombination. It was previously shown that in vitro BLM helicase promotes disruption of recombination intermediates, regression of stalled replication forks, and dissolution of double Holliday junctions. Here, we demonstrate two novel activities of BLM: disruption of the Rad51-ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) filament, an active species that promotes homologous recombination, and stimulation of DNA repair synthesis. Using in vitro reconstitution reactions, we analyzed how different biochemical activities of BLM contribute to its functions in homologous recombination.
Figures

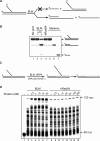
Similar articles
-
The Bloom's syndrome gene product promotes branch migration of holliday junctions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 6;97(12):6504-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.100448097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10823897 Free PMC article.
-
BLAP75/RMI1 promotes the BLM-dependent dissolution of homologous recombination intermediates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 14;103(11):4068-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508295103. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537486 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction between the Bloom's syndrome helicase and the RAD51 paralog, RAD51L3 (RAD51D).J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 28;278(48):48357-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308838200. Epub 2003 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12975363
-
Functions of RecQ family helicases: possible involvement of Bloom's and Werner's syndrome gene products in guarding genome integrity during DNA replication.J Biochem. 2001 Apr;129(4):501-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002883. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11275547 Review.
-
Role of the BLM helicase in replication fork management.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):936-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17363339 Review.
Cited by
-
Human RECQL5: guarding the crossroads of DNA replication and transcription and providing backup capability.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 May-Jun;48(3):289-99. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.792770. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23627586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of direct replication restart at stressed replisomes.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Nov;95:102947. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102947. Epub 2020 Aug 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32853827 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Top3-Rmi1 dissolve Rad51-mediated D loops by a topoisomerase-based mechanism.Mol Cell. 2015 Feb 19;57(4):595-606. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.022. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25699708 Free PMC article.
-
Rif1 provides a new DNA-binding interface for the Bloom syndrome complex to maintain normal replication.EMBO J. 2010 Sep 15;29(18):3140-55. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.186. Epub 2010 Aug 13. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20711169 Free PMC article.
-
Human RAD51 paralogue SWSAP1 fosters RAD51 filament by regulating the anti-recombinase FIGNL1 AAA+ ATPase.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 29;10(1):1407. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09190-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30926776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams M.D., McVey M., Sekelsky J.J., McVey M., Sekelsky J.J., Sekelsky J.J. Drosophila BLM in double-strand break repair by synthesis-dependent strand annealing. Science. 2003;299:265–267. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S., Tafel A.A., Kanaar R., Tafel A.A., Kanaar R., Kanaar R. DNA double-strand break repair and chromosome translocations. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2006;5:1075–1081. - PubMed
-
- Allers T., Lichten M., Lichten M. Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell. 2001;106:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Amitani I., Baskin R.J., Kowalczykowski S.C., Baskin R.J., Kowalczykowski S.C., Kowalczykowski S.C. Visualization of Rad54, a chromatin remodeling protein, translocating on single DNA molecules. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:143–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
