IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling and the inflammasome are essential in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 17992263
- PMCID: PMC2066195
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32285
IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling and the inflammasome are essential in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice
Abstract
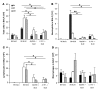
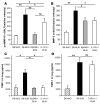
The molecular mechanisms of acute lung injury resulting in inflammation and fibrosis are not well established. Here we investigate the roles of the IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1) and the common adaptor for Toll/IL-1R signal transduction, MyD88, in this process using a murine model of acute pulmonary injury. Bleomycin insult results in expression of neutrophil and lymphocyte chemotactic factors, chronic inflammation, remodeling, and fibrosis. We demonstrate that these end points were attenuated in the lungs of IL-1R1- and MyD88-deficient mice. Further, in bone marrow chimera experiments, bleomycin-induced inflammation required primarily MyD88 signaling from radioresistant resident cells. Exogenous rIL-1beta recapitulated a high degree of bleomycin-induced lung pathology, and specific blockade of IL-1R1 by IL-1 receptor antagonist dramatically reduced bleomycin-induced inflammation. Finally, we found that lung IL-1beta production and inflammation in response to bleomycin required ASC, an inflammasome adaptor molecule. In conclusion, bleomycin-induced lung pathology required the inflammasome and IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling, and IL-1 represented a critical effector of pathology and therapeutic target of chronic lung inflammation and fibrosis.
Figures
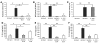
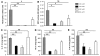
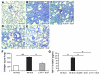
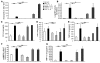
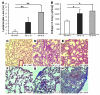

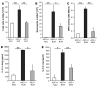
Similar articles
-
Fluorofenidone attenuates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via inhibiting the activation of NALP3 inflammasome and IL-1β/IL-1R1/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Nov;20(11):2064-2077. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12898. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27306439 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling is critical for elastase-induced lung inflammation and emphysema.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 15;183(12):8195-202. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803154. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 20007584
-
Postoperative ileus involves interleukin-1 receptor signaling in enteric glia.Gastroenterology. 2014 Jan;146(1):176-87.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.030. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24067878
-
Procoagulant signalling mechanisms in lung inflammation and fibrosis: novel opportunities for pharmacological intervention?Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S367-78. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707603. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18223674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009 May-Jun;57(3):165-76. doi: 10.1007/s00005-009-0024-y. Epub 2009 May 29. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009. PMID: 19479203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parvovirus B19 in Rheumatic Diseases.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 19;12(8):1708. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081708. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-1β-activated PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways coordinately promote induction of partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 8;22(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01775-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39118068 Free PMC article.
-
Immune mechanisms in fibrotic interstitial lung disease.Cell. 2024 Jul 11;187(14):3506-3530. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.015. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38996486 Review.
-
Extracellular glucose triggers metabolic reprogramming of cultured human bronchial epithelial cells and indirect fibroblast activation.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Sep;14(9):1441-1454. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13852. Epub 2024 Jul 1. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 38952051 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in a murine model of acute lung injury.Exp Physiol. 2024 Jun;109(6):966-979. doi: 10.1113/EP091682. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38594909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gross T.J., Hunninghake G.W. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;345:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Piguet P.F. Cytokines involved in pulmonary fibrosis. Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 1993;34:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Keane M.P., Strieter R.M., Belperio J.A. Mechanisms and mediators of pulmonary fibrosis. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2005;25:429–463. - PubMed
-
- Beeh K.M., Beier J., Kornmann O., Buhl R. Sputum matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloprotinease-1, and their molar ratio in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and healthy subjects. Respir. Med. 2003;97:634–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

