DLC-1:a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor
- PMID: 17979893
- PMCID: PMC4401278
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00098.x
DLC-1:a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor
Abstract
The deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC-1) gene encodes a GTPase activating protein that acts as a negative regulator of the Rho family of small GTPases. Rho proteins transduce signals that influence cell morphology and physiology, and their aberrant up-regulation is a key factor in the neoplastic process, including metastasis. Since its discovery, compelling evidence has accumulated that demonstrates a role for DLC-1 as a bona fide tumour suppressor gene in different types of human cancer. Loss of DLC-1 expression mediated by genetic and epigenetic mechanisms has been associated with the development of many human cancers, and restoration of DLC-1 expression inhibited the growth of tumour cells in vivo and in vitro. Two closely related genes, DLC-2 and DLC-3, may also be tumour suppressors. This review presents the current status of progress in understanding the biological functions of DLC-1 and its relatives and their roles in neoplasia.
Figures

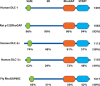
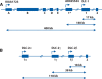

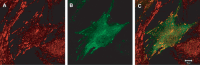
Similar articles
-
Identifying Cancer-Relevant Mutations in the DLC START Domain Using Evolutionary and Structure-Function Analyses.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 31;21(21):8175. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218175. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142932 Free PMC article.
-
Deleted in liver cancer 3 (DLC-3), a novel Rho GTPase-activating protein, is downregulated in cancer and inhibits tumor cell growth.Oncogene. 2007 Jul 5;26(31):4580-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210244. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17297465
-
The Role of Tumor Suppressor DLC-1: Far From Clear.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(7):896-901. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160907142754. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27604574 Review.
-
Expression profile of the tumor suppressor genes DLC-1 and DLC-2 in solid tumors.Int J Oncol. 2006 Nov;29(5):1127-32. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17016643
-
StarD13: a potential star target for tumor therapeutics.Hum Cell. 2020 Jul;33(3):437-443. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00358-2. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 32274657 Review.
Cited by
-
Tensin1 requires protein phosphatase-1alpha in addition to RhoGAP DLC-1 to control cell polarization, migration, and invasion.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 11;284(50):34713-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.059592. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19826001 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Transcriptomic Signatures in Pediatric and Adult CML.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 14;13(24):6263. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246263. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944883 Free PMC article.
-
DLC1 tumor suppressor gene inhibits migration and invasion of multiple myeloma cells through RhoA GTPase pathway.Leukemia. 2009 Feb;23(2):383-90. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.285. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Leukemia. 2009. PMID: 18923442 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated serum response factor triggers formation of hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2015 Mar;61(3):979-89. doi: 10.1002/hep.27539. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25266280 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis and Tumor Vasculature.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 4;10:612802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.612802. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33614496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Van Aelst L, D'Souza-Schorey C. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2295–322. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:471–7. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho-GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:247–69. - PubMed
-
- Sahai E, Marshall CJ. Rho-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:133–42. - PubMed
-
- Gomez del Pulgar T, Benitah SA, Valeron PF, Espina C, Lacal JC. Rho GTPase expression in tumourigenesis: evidence for a significant link. Bioessays. 2005;27:602–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

