Antagonistic nature of T helper 1/2 developmental programs in opposing peripheral induction of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells
- PMID: 17978190
- PMCID: PMC2084315
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0703642104
Antagonistic nature of T helper 1/2 developmental programs in opposing peripheral induction of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells
Abstract
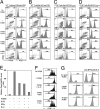
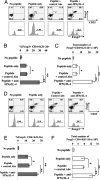
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of peripheral induction of Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the dominant control of immunological tolerance. However, Foxp3(+) Treg differentiation from naïve CD4(+) T cells occurs only under selective conditions, whereas the classical T helper (Th) 1 and 2 effector development often dominate T cell immune responses to antigen stimulation in the periphery. The reason for such disparity remains poorly understood. Here we report that Th1/Th2-polarizing cytokines can potently inhibit Foxp3(+) Treg differentiation from naïve CD4(+) precursors induced by TGF-beta. Furthermore, antigen receptor-primed CD4(+) T cells are resistant to Treg induction because of autocrine production of IFNgamma and/or IL-4, whereas neutralizing IFNgamma and IL-4 not only can potentiate TGF-beta-mediated Foxp3 induction in vitro but can also enhance antigen-specific Foxp3(+) Treg differentiation in vivo. Mechanistically, inhibition of Foxp3(+) Treg development by Th1/Th2-polarizing cytokines involves the activation of Th1/Th2 lineage transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 through the canonical Stat1-, Stat4-, and Stat6-dependent pathways. Using IFNgamma and IL-4 knockouts and retrovirus-mediated transduction of T-bet and GATA-3, we further demonstrate that enforced expression of the Th1/Th2 lineage-specific transcription factors is sufficient to block Foxp3 induction and Treg differentiation independent of the polarizing/effector cytokines. Thus, our study has unraveled a previously unrecognized mechanism of negative cross-regulation of Foxp3(+) Treg fate choice by Th1/Th2 lineage activities. In addition, these findings also provide an attainable explanation for the general paucity of antigen-triggered de novo generation of Foxp3(+) Tregs in the periphery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
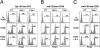

Similar articles
-
Induction of antigen specific CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+)T regulatory cells from naïve natural thymic derived T regulatory cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Oct;28(2):875-86. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.03.049. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25882104
-
An intrinsic mechanism predisposes Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells to Th2 conversion in vivo.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 15;185(10):5983-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001255. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20944002 Free PMC article.
-
Immune suppressive activity and lack of T helper differentiation are differentially regulated in natural regulatory T cells.J Immunol. 2009 Sep 15;183(6):3583-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900146. Epub 2009 Aug 26. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19710452
-
Distinct regulatory CD4+T cell subsets; differences between naïve and antigen specific T regulatory cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Oct;23(5):641-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21840184 Review.
-
Translational mini-review series on Th17 cells: induction of interleukin-17 production by regulatory T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Feb;159(2):120-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04038.x. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19912251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allergic conjunctivitis renders CD4(+) T cells resistant to t regulatory cells and exacerbates corneal allograft rejection.Am J Transplant. 2013 May;13(5):1181-92. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12198. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23489547 Free PMC article.
-
Microbe-dendritic cell dialog controls regulatory T-cell fate.Immunol Rev. 2010 Mar;234(1):305-16. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00880.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20193027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interruption of dendritic cell-mediated TIM-4 signaling induces regulatory T cells and promotes skin allograft survival.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):4447-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300992. Epub 2013 Sep 13. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24038092 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning microenvironments: induction of regulatory T cells by dendritic cells.Immunity. 2008 Sep 19;29(3):362-71. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.005. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 18799144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD62L(neg)CD38⁺ expression on circulating CD4⁺ T cells identifies mucosally differentiated cells in protein fed mice and in human celiac disease patients and controls.Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1147-59. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.24. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21386831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glimcher LH, Murphy KM. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1693–1711. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KM, Reiner SL. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:933–944. - PubMed
-
- Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Gavrieli M, Murphy KM. Immunity. 2006;24:677–688. - PubMed
-
- Jaeckel E, Kretschmer K, Apostolou I, von Boehmer H. Semin Immunol. 2006;18:89–92. - PubMed
-
- Lohr J, Knoechel B, Abbas AK. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:149–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

