Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) regulates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression in microglia
- PMID: 17961202
- PMCID: PMC2423670
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04838.x
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) regulates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression in microglia
Abstract
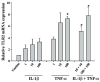
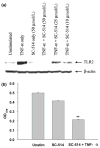
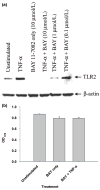
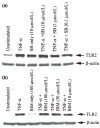
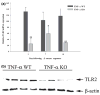
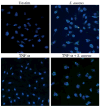
Microglia represent one effector arm of CNS innate immunity as evident by their role in pathogen recognition. We previously reported that exposure of microglia to Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), a prevalent CNS pathogen, led to elevated Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) expression, a pattern recognition receptor capable of recognizing conserved structural motifs associated with gram-positive bacteria such as S. aureus. In this study, we demonstrate that the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) enhances TLR2 expression in microglia, whereas interleukin-1beta has no significant effect. To determine the downstream signaling events responsible for elevated microglial TLR2 expression in response to TNF-alpha, a series of signal transduction inhibitors were employed. Treatment with caffeic acid phenethyl ester, an inhibitor of redox-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B activation, significantly attenuated TNF-alpha-induced TLR2 expression. Similar results were observed with the IKK-2 and IkappaB-alpha inhibitors SC-514 and BAY 11-7082, respectively. In contrast, no significant alterations in TLR2 expression were observed with protein kinase C or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors. A definitive role for TNF-alpha was demonstrated by the inability of S. aureus to augment TLR2 expression in microglia isolated from TNF-alpha knockout mice. In addition, TLR2 expression was significantly attenuated in brain abscesses of TNF-alpha knockout mice. Collectively, these results indicate that in response to S. aureus, TNF-alpha acts in an autocrine/paracrine manner to enhance TLR2 expression in microglia and that this effect is mediated, in part, by activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TLR2 expression in astrocytes is induced by TNF-alpha- and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 15;181(6):3841-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3841. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18768838 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidoglycan enhances proinflammatory cytokine expression through the TLR2 receptor, MyD88, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and NF-kappaB pathways in BV-2 microglia.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Aug;10(8):883-91. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.04.026. Epub 2010 May 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20451669
-
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)-TLR9 crosstalk dictates IL-12 family cytokine production in microglia.Glia. 2012 Jan;60(1):29-42. doi: 10.1002/glia.21243. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Glia. 2012. PMID: 21901759 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent roles for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the brain.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;2(2):140-53. doi: 10.1007/s11481-007-9070-6. Epub 2007 Mar 31. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18040839 Review.
-
Autocrine positive feedback of tumor necrosis factor from activated microglia proposed to be of widespread relevance in chronic neurological disease.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2023 Oct;11(5):e01136. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1136. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2023. PMID: 37750203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor 2 mediates vascular contraction and activates RhoA signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells from STZ-induced type 1 diabetic rats.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Nov;467(11):2361-74. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1688-2. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25600901
-
Monocytes enhance the inflammatory response to TLR2 stimulation in aortic valve interstitial cells through paracrine up-regulation of TLR2 level.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 3;16(15):3062-3074. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.49332. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33061818 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-specific TLR2 signaling mediates pathogen-induced TNF-dependent inflammatory oral bone loss.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 1;190(3):1148-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202511. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23264656 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1RI (interleukin-1 receptor type I) signalling is essential for host defence and hemichannel activity during acute central nervous system bacterial infection.ASN Neuro. 2012 Apr 18;4(3):e00085. doi: 10.1042/AN20120008. ASN Neuro. 2012. PMID: 22414156 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors in brain abscess.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;336:41-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00549-7_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19688327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F. Immune function of microglia. Glia. 2001;36:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS. A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature. 2003;423:659–663. - PubMed
-
- Beg AA, Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science. 1996;274:782–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 RR019395/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH065297-04/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH065297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055385-05A2/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019395-01A1/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH65297/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR19395/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047546-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS055385/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047546/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047546-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR6460/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055385/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047546-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

