Enhancing the anti-angiogenic action of histone deacetylase inhibitors
- PMID: 17958916
- PMCID: PMC2173905
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-6-68
Enhancing the anti-angiogenic action of histone deacetylase inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) have many effects on cancer cells, such as growth inhibition, induction of cell death, differentiation, and anti-angiogenesis, all with a wide therapeutic index. However, clinical trials demonstrate that HDACIs are more likely to be effective when used in combination with other anticancer agents. Moreover, the molecular basis for the anti-cancer action of HDACIs is still unknown. In this study, we compared different combinations of HDACIs and anti-cancer agents with anti-angiogenic effects, and analysed their mechanism of action.
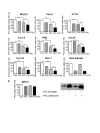
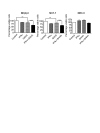
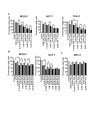
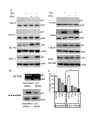
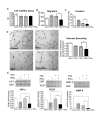
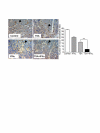
Results: Trichostatin A (TSA) and alpha-interferon (IFNalpha) were the most effective combination across a range of different cancer cell lines, while normal non-malignant cells did not respond in the same manner to the combination therapy. There was a close correlation between absence of basal p21WAF1 expression and response to TSA and IFNalpha treatment. Moreover, inhibition of p21WAF1 expression in a p21WAF1-expressing breast cancer cell line by a specific siRNA increased the cytotoxic effects of TSA and IFNalpha. In vitro assays of endothelial cell function showed that TSA and IFNalpha decreased endothelial cell migration, invasion, and capillary tubule formation, without affecting endothelial cell viability. TSA and IFNalpha co-operatively inhibited gene expression of some pro-angiogenic factors: vascular endothelial growth factor, hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and matrix metalloproteinase 9, in neuroblastoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Combination TSA and IFNalpha therapy markedly reduced tumour angiogenesis in neuroblastoma-bearing transgenic mice.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that combination TSA and IFNalpha therapy has potent co-operative cytotoxic and anti-angiogenic activity. High basal p21WAF1 expression appears to be acting as a resistance factor to the combination therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 inhibits angiogenesis and has a greater antitumor effect in combination with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584.Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 15;64(18):6626-34. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0540. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15374977
-
Mechanisms of cell death induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors in androgen receptor-positive prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2006 Feb;4(2):113-23. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0085. Mol Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16513842
-
Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor suppresses NADPH Oxidase 4-Derived Redox Signalling and Angiogenesis.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Oct;20(10):1932-44. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12885. Epub 2016 Jun 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27297729 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor activates the p21/WAF1/Cip1 gene promoter through the Sp1 sites.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;886:195-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb09415.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10667218 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase as a new target for cancer chemotherapy.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;48 Suppl 1:S20-6. doi: 10.1007/s002800100300. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11587361 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of chromatin structure in cell migration.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;21(1):6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.09.002. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20951589 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid blocks adhesion of renal cell carcinoma cells to endothelium and extracellular matrix.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Aug;13(8B):2342-2352. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00603.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19067765 Free PMC article.
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid alters growth properties of renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Aug;13(8B):2376-2385. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00436.x. Epub 2008 Jul 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 18657224 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: potential targets responsible for their anti-cancer effect.Invest New Drugs. 2010 Dec;28 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S3-20. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9596-y. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Invest New Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21161327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of epigenetic regulators in neuroblastoma.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Apr 27;50(4):1-12. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0077-2. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29700278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

