Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 17951530
- PMCID: PMC2214773
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-04-087734
Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
Abstract
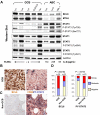
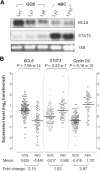
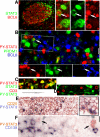
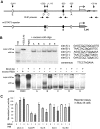
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) consists of at least 2 phenotypic subtypes; that is, the germinal center B-cell-like (GCB-DLBCL) and the activated B-cell-like (ABC-DLBCL) groups. It has been shown that GCB-DLBCL responds favorably to chemotherapy and expresses high levels of BCL6, a transcription repressor known to play a causative role in lymphomagenesis. In comparison, ABC-DLBCL has lower levels of BCL6, constitutively activated nuclear factor-kappaB, and tends to be refractory to chemotherapy. Here, we report that the STAT3 gene is a transcriptional target of BCL6. As a result, high-level STAT3 expression and activation are preferentially detected in ABC-DLBCL and BCL6-negative normal germinal center B cells. Most importantly, inactivating STAT3 by either AG490 or small interference RNA in ABC-DLBCL cells inhibits cell proliferation and triggers apoptosis. These phenotypes are accompanied by decreased expression of several known STAT3 target genes, including c-Myc, JunB, and Mcl-1, and increased expression of the cell- cycle inhibitor p27. In addition to identifying STAT3 as a novel BCL6 target gene, our results define a second oncogenic pathway, STAT3 activation, which operates in ABC-DLBCL, suggesting that STAT3 may be a new therapeutic target in these aggressive lymphomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
BCL6 programs lymphoma cells for survival and differentiation through distinct biochemical mechanisms.Blood. 2007 Sep 15;110(6):2067-74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-069575. Epub 2007 Jun 1. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17545502 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma.Nature. 2011 Feb 3;470(7332):115-9. doi: 10.1038/nature09671. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21179087 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3701-13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-111948. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18160665 Free PMC article.
-
The Expanding Role of the BCL6 Oncoprotein as a Cancer Therapeutic Target.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Feb 15;23(4):885-893. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2071. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27881582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: the old and the new.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011 Jun;11 Suppl 1:S87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2011.03.029. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011. PMID: 22035756 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I study of a novel oral Janus kinase 2 inhibitor, SB1518, in patients with relapsed lymphoma: evidence of clinical and biologic activity in multiple lymphoma subtypes.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Nov 20;30(33):4161-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.5223. Epub 2012 Sep 10. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22965964 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Loss of PRDM1/BLIMP-1 function contributes to poor prognosis of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Leukemia. 2017 Mar;31(3):625-636. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.243. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 27568520 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function mutations in PTPN6 promote STAT3 deregulation via JAK3 kinase in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44703-13. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6300. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26565811 Free PMC article.
-
Cerdulatinib, a novel dual SYK/JAK kinase inhibitor, has broad anti-tumor activity in both ABC and GCB types of diffuse large B cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 22;6(41):43881-96. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6316. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26575169 Free PMC article.
-
JAK1/2 Inhibitors AZD1480 and CYT387 Inhibit Canine B-Cell Lymphoma Growth by Increasing Apoptosis and Disrupting Cell Proliferation.J Vet Intern Med. 2017 Nov;31(6):1804-1815. doi: 10.1111/jvim.14837. Epub 2017 Sep 27. J Vet Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28960447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stein H, Dallenbach F. Diffuse large cell lymphoma of B and T cell type. In: Knowles DM, editor. Neoplastic Hematopathology. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; 1992. pp. 675–714.
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1937–1947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

